With the development of technology, the NVH performance of automobile engines, drivelines, and interior parts is gradually improved, the NVH problem of the steering system is gradually highlighted, and the steering NVH problem is easily perceived by drivers and causes complaints. Therefore, it is urgent to study the NVH problem of the steering systems, and how to improve the NVH performance of steering systems is also a key research direction in the product development process.
This paper describes a hydraulic noise generated by the hydraulic steering rack at the limit of rudder return, proposes the improvement direction through mechanism analysis, and proves that the method is feasible through real vehicle verification.
1 Working principle of the power steering system
The car steering system is an important system to control the driving direction of the car. The car steering system directly affects the stability and maneuverability of the car. In addition to the requirement of its light handling, safety, and reliability, it also requires that it can work normally under different working conditions in accordance with the driver’s operation and provide the best road sense.
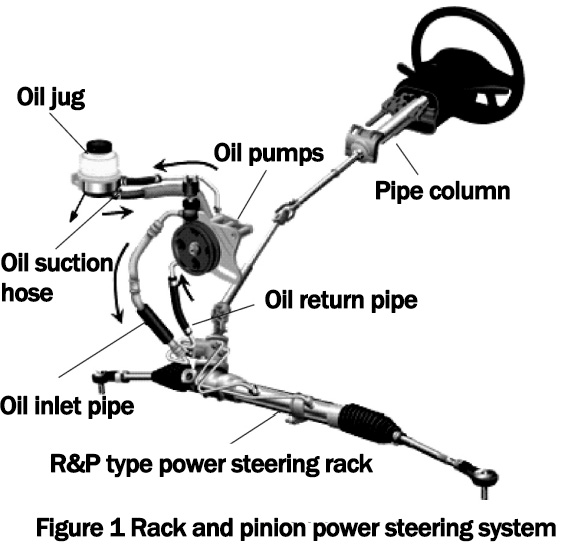
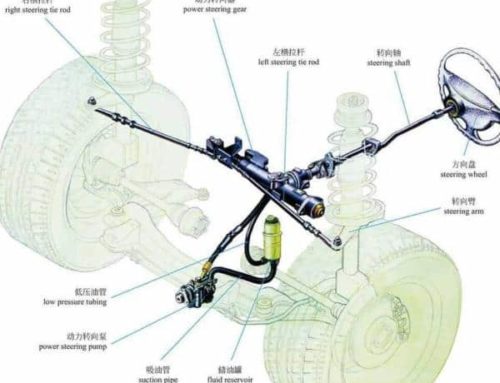
The power steering system is added to the traditional mechanical steering system, and at this stage, there are mainly two kinds of power systems: hydraulic and electric. The hydraulic power steering system is described in this article, which consists of a power steering rack, steering wheel, pipe column, high and low-pressure oil pipe, oil pot, etc., as shown in Figure 1. The working principle is that the oil pump is driven by the engine to suck oil from the oil pot, and through the oil pump vane, the oil is pumped out to provide power to the steering gear, and the steering gear controls the flow of oil according to the internal valve assembly, so as to realize left and right steering and straight travel, and then the oil returns to the oil pot through the steering rack return port, completing a cycle. The power steering system is an important sub-power of the steering system. The power steering system is added to the traditional mechanical steering system, and at this stage, there are mainly two power systems: hydraulic and electric. The working principle is that the oil pump is driven by the engine to suck oil from the oil pot, and through the oil pump vane, the oil is pumped out to provide power to the steering rack, and the steering gear controls the flow of oil according to the internal valve assembly, so as to realize left and right steering and straight travel, and then the oil returns to the oil pot through the steering gear return port, completing a cycle. The power steering unit is an important sub-system of the steering system.
2 Mechanism and improvement plan of hydraulic rudder reverberation of hydraulic steering limit
(1) Mechanism of hydraulic rudder reverberation of hydraulic steering rack limit
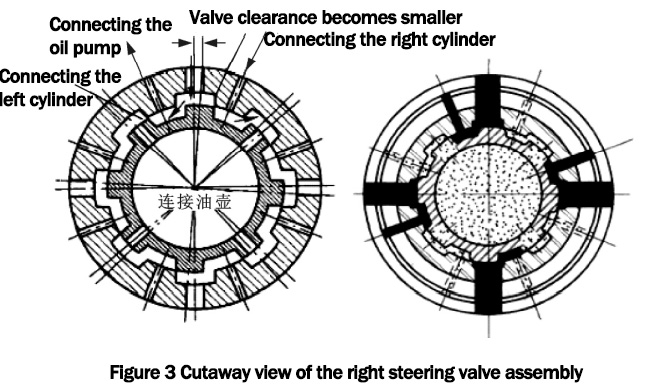
Figure 3 shows the cross-sectional view of the right steering valve assembly. When the vehicle is steered in place to a position close to the limit, the gap between the right spool and the valve sleeve becomes smaller, most of the flow from the oil pump enters the left cylinder, and the pressure of the steering system is close to the working pressure limit at this time. The change of pressure from high to low will produce a hydraulic shock, resulting in hydraulic fluctuations in the steering system, and then produce The change in pressure from high to low will produce a hydraulic shock, leading to hydraulic fluctuations in the steering system, which will produce a strange noise.
2) Improvement solution
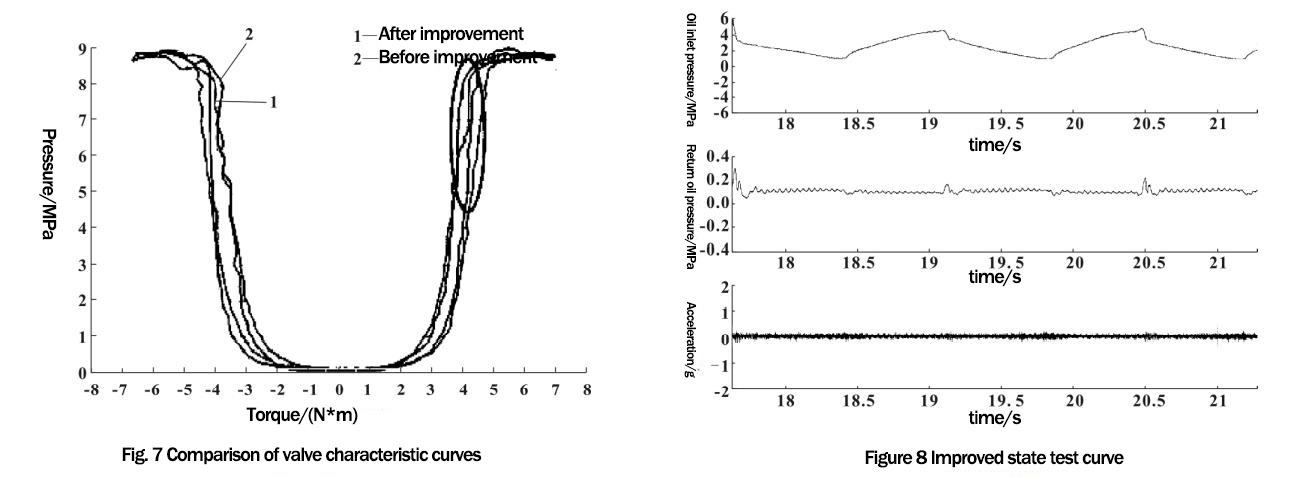
The fundamental solution to the limit back to the rudder noise is to reduce the hydraulic shock, and the size of the hydraulic shock and the size of the flow, torsion bar stiffness, the change in valve clearance cross-sectional area between the valve spool valve sleeve. Reduce the flow rate of the steering system, may lead to fast play directional sink new failure, in engineering applications are often used by changing the valve plane parameters to achieve the valve clearance cross-sectional area change, reduce the pressure shock, this method can ensure that the system flow does not reduce the torsion bar stiffness does not change the case to solve the noise and minimize the impact of manipulation stability performance. The effect of the valve plane parameter can be directly reflected in the valve characteristic curve, as shown in Figure 4, reducing the shock is also reduces the slope of the rudder curve
3 Complete vehicle testing
1) Equipment of the digital acquisition system
In this paper, the test of the real vehicle was conducted using the digital acquisition equipment (8 channels) of the Oriental Institute. The main equipment of the test is listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Main equipment for testing
| No. | Name | Type | Factory |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Acceleration sensor | 356A32 | PCB |
| 2 | Oil pressure sensor | CYB-20S | Vester |
| 3 | Data Collector | 3060C | Oriental Institute |
| 4 | Analysis System | DASP V11 | Oriental Institute |
2 ) Sensor connection
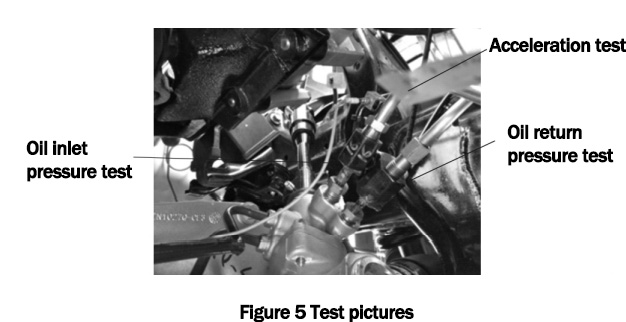
Because the noise is generated by the hydraulic shock, the steering fluid pressure is the key test object. The acceleration test was carried out on the steering tube, as shown in Figure 5.
4 Analysis of test results
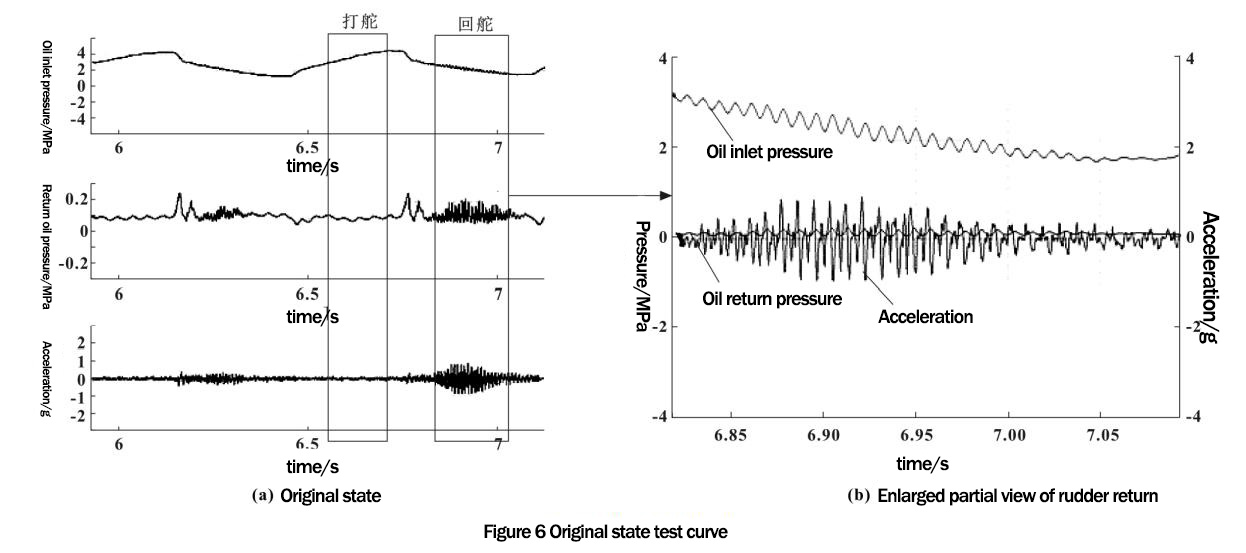
The curves of steering oil inlet, oil return, and acceleration were all normal during rudder. However, the curves of all three curves showed abnormal fluctuation and were accompanied by abnormal noise when returning to the rudder, which was consistent with the fault phenomenon. When the curves are amplified, the three waveforms match, indicating that the noise is caused by the fluctuation of hydraulic shock. The waveforms of the three curves match, indicating that the noise is caused by the fluctuation of the hydraulic shock, as shown in Figure 6.
After optimizing the valve plane parameters and reducing the slope of the rudder return curve (Figure 7), only the steering valve assembly was replaced and the rest of the components were left unchanged, and the test was conducted again according to the original test condition. On the one hand, it proves that the hydraulic noise of the rudder can be effectively suppressed by changing the valve plane parameters, and on the other hand, it proves that this test method is effective.
5 Conclusion
The analysis in this paper shows that when the hydraulic steering system has a rudder return near the limit hydraulic noise fault, the valve plane parameters can be changed to eliminate the noise effectively. This improvement solution has the advantages of a short improvement period and a limited impact on the performance of the steering system. This improvement plan has the advantages of a short improvement period and limited impact on the performance of the steering system, which provides a reference for solving such problems.
(We do not share your data with anybody, and only use it for its intended purpose)
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?






Leave A Comment