Among the three basic functions of a vehicle, “driving, steering, and stopping,” the steering mechanism controls “steering” and is an important device for controlling “steering performance,” which is the most important function of a vehicle. Looking back at the history of the gradual spread of vehicles, the emergence of power steering has made steering operations easier and is a major device that assists drivers in driving comfortably, just like automatic transmissions and onboard air conditioning.
Initially, power steering was only available on some premium models and was a high-end feature, but as front-wheel-drive vehicles became more popular, the front wheels with drive function made steering heavy, and power steering with assisted steering became widely used, and now in the Japanese market, most passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and minivans are equipped with power steering as standard.
1 Outline
Micro cars and small cars account for a large proportion of the Japanese market, and their engine output is low compared to that of medium and large passenger cars, making them unsuitable for hydraulic power steering systems. As a result, electric power steering (EPS), which uses small electric motors to assist in steering by electrifying hydraulic devices and eliminating piping and other components, was first installed in minivans and gradually spread. In addition, since the conclusion of the Kyoto Protocol in 2005, the automotive industry has been working to reduce CO2 emissions as a major countermeasure to improve fuel efficiency, and electric power steering systems, together with continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) and idle-stop systems, have also played an important role in accelerating the spread of electric power steering from midsize cars to large cars.
As a result, most models in the Japanese market are equipped with power steering, and most models, except for some commercial vehicles and some premium cars and sports cars with sufficient engine output and emphasis on steering performance, have switched from hydraulic power steering (hydraulic pump drive) to electric power steering (electric motor assist) as an opportunity for model changes. Currently, more than half of passenger cars have electric power steering systems.
In addition, electric power steering is indispensable for the coordination of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) such as lane departure warning system (LDW) and lane-keeping assist system (LKA) with steering operations (operation assistance, reverse control).
In addition, in recent years, each vehicle manufacturer has been working on the development of autonomous driving systems, and further improvements in the functions and performance of electric steering systems will be sought in the future. In addition, the high performance and complexity of electric and electronic automotive components have been growing rapidly in recent years, and it is increasingly important that these components and systems function safely without failures or operating errors, so that cars can be driven safely. In EPS, failure modes such as steering lock are classified as the most stringent ASIL D. EPS requires high quality in terms of functional safety and lengthy design.
The following is a description of the classification according to the mode of assistance.
Hydraulic power steering systems are divided into two main types:
- Conventional hydraulic power steering (HPS): A conventional steering system that converts part of the dynamic output of the engine (including electronically controlled) into hydraulic pump pressure and is driven by a hydraulic pump. A conventional steering system that converts part of the dynamic output of the engine (including electric) into hydraulic pump pressure and is driven by the hydraulic pump
- Electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS): Electric motor-driven hydraulic pump, only for premium cars and sports cars
Electric power steering systems can be divided into three main types depending on the installation position of the drive source motor:
- Column-assisted EPS (C-EPS): Mounted on the side of the steering column in the vehicle, driving the steering column shaft
Advantages:
- The motor is mounted in the cockpit to ensure sufficient space in the engine compartment, mainly for micro cars and small cars
- Waterproof
Disadvantages:
- Small motor size, difficult to increase output power
- The motor is inside the cockpit, so it is noisy
- The steering operation is easy to feel unpleasant
- Rack-assisted EPS (R-EPS): mounted in the rack box in the engine compartment and directly driven by the rack. There are two types: the “Rack and pinion type (RD-EPS)”, in which the motor and rack and pinion are placed on the same shaft; the “Rack Cross type (Rack Cross) (RC-EPS)”, in which the rack and pinion shafts are placed at an angle; and the “Rack Parallel type”, in which the rack and pinion shafts are placed in parallel. Rack and pinion parallel type (Rack Parallel type and Belt drive type) (RP-EPS)” with parallel gear shafts.
Advantages:
- Good steering feel due to direct drive of rack and pinion
- Low noise level because the motor is not located in the cockpit
- Good for increasing output power, suitable for large passenger cars and sports cars
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost takes up space in the engine compartment, needs to consider waterproof countermeasures
- Gear-assisted EPS (P-EPS/DP-EPS): P-EPS, which is installed in the gearbox of the engine compartment and drives the pinion, and DP-EPS, which is a two-gear rack-and-pinion structure that separates the power-assisted mechanism from the handle shaft and responds to increased vehicle maneuverability and high power output.
Advantages:
- Better steering feel than column-assisted type
- Low noise level because the motor is not located in the cockpit
- Good for increasing power output, suitable for large passenger cars and sports cars
Disadvantages:
- Takes up space in the engine compartment, and requires consideration of waterproof countermeasures
- Compared with the rack-assisted type, the gear-assisted type imposes a greater load on the rack and pinion mechanism.
In Part VI, “Product Support”, the above-mentioned three driving methods of conventional hydraulic, electro-hydraulic and electric power steering and the three auxiliary methods of electric power steering are described in detail as far as possible. Power steering systems include not only steering mechanisms but also structural components, including hydraulic pumps for conventional hydraulics and electrohydraulic, motors for electric power steering, and ECUs for all power steering systems except mechanical hydraulics. The above structural components will therefore be mentioned as appropriate in the “Summary of Major Power Steering Component Suppliers” in Part 2.
In recent years, there has been a trend toward electromechanical integration of the ECU and motor into the steering mechanism (power unit), and brushless motors, which are advantageous for redundant design in response to safety functions (redundant structural design is not possible with brushes (a structure with two commutators and brushes on both sides is required). ). In addition, the Nissan Skyline V37, which was launched in February 2014, is equipped with DAS wire-controlled active steering technology as an option, which means that the power steering system, which is already commonly fitted as standard, is still being improved.
2 Summary of major power steering component suppliers
The main Japanese suppliers of power steering components for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles are JTEKT, NSK Steering Systems, Hitachi Automotive Systems, KYB, and Showa. In addition, foreign suppliers for some models in the Japanese market include Trina and Robert Bosch Automotive Steering Co.
Among them, there are only four suppliers of hydraulic power steering systems for Japanese OEMs in the Japanese market, namely JTEKT, Hitachi Automotive Systems, KYB, and Trina.
In recent years, Nestea Automotive Systems has been developing C-EPS (including battery pack) for Suzuki mass production, and Mando is developing C-EPS (including battery pack) for Honda 18Brio mass production as a secondary source for JTEKT.
1) JTEKT
Koyo Seiko was established in January 2006 through the merger of Koyo Seiko and Toyota Kogyo. The company is part of Toyota and is the largest supplier of power steering in Japan. It has a share of about 60% in the domestic power steering market. (Domestic share EPS 69.3%, HPS 43% in 2014)
We have a capital and business tie-up with Fuji Kikoh, a former Nissan subsidiary that produces steering columns, and supplies a wide range of products to vehicle manufacturers other than Toyota. Koyo Seiko
In 1988, Koyo Seiko was the first in the world to successfully mass-produce the now popular electric power steering system, which was installed in the minicar Suzuki Cervo (CG72V/CH72V).
We produce three types of electric power steering systems: conventional hydraulic, electro-hydraulic, and electric power steering systems, and we mass-produce column power steering systems (C-EPS) and gear power steering systems (DP-EPS/P-EPS) for micro-, small-, and medium-sized cars, and rack power steering systems (RP-EPS/RD-EPS) for medium- and large-sized passenger cars and sports cars.
In April 2015, the cumulative global production of electric power steering systems (EPS) reached 100 million units in April. At present, JTEKT supplies EPS to more than 15 vehicle manufacturers, securing its No. 1 position with a global market share of more than 30%.
For the steering column-assisted EPS (C-EPS), mass production of the integrated motor/ECU for C-EPS began at the Garden Plant in 2012.
Steering system structural component suppliers
- ECU/motor: Toyota, Daihatsu, and Fuji Heavy Industries are mainly supplied by Denso, while Nissan and Mazda are mainly supplied by Mitsubishi Electric.
- Hydraulic pumps are mainly produced in-house, while some are produced by other suppliers such as KYB.
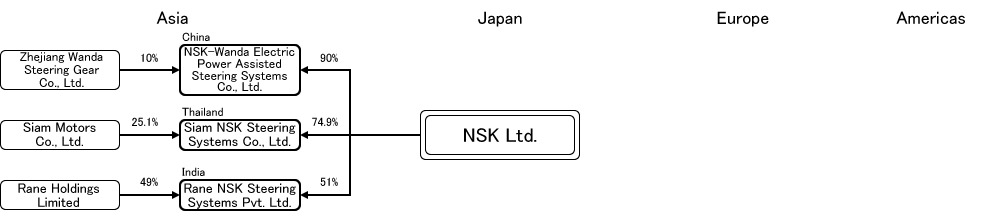
2) NSK Steering Systems
In 2001, a major bearing company, Nippon Seiko Corporation, spun off its electric power steering business and established a subsidiary, NSK Steering Systems (Co., Ltd.). The following year, in 2002, the entire steering business was transferred and integrated into the company, establishing its foundation as a steering system supplier.
NSK ranks second in the Japanese power steering market after Jettagit, but has a much smaller share than Jettagit, with a share of about 15%.
Only electric power steering systems are produced. Among the three types of assistance, we supply column-assisted steering systems (C-EPS) for micro, small and medium-sized cars, and rack-assisted steering systems (R-EPS) and gear-assisted steering systems (P-EPS) for large passenger cars and sports cars. However, C-EPS and P-EPS are the ones with actual performance in mass production.(Domestic share EPS 19.6%, HPS 0% in 2014)
We have eight production plants in six countries: Japan (headquarters in Poland and Akagi Plant), the United States, Poland, India, Thailand, and China (Dongguan and Hangzhou). In recent years, in addition to transferring EPS production from the UK to Poland and starting production in Thailand in 2011, we have also expanded production capacity in China and India.
In January 2016, we announced the development of the industry’s lightest column-type electric power steering system (C-EPS). By reducing the size of the torque sensor and reduction gear, the overall weight of the EPS assembly has been reduced by 13% compared to the previous one. At the same time, the torque sensor function has been enhanced, and safety has been improved by adding functions to ensure proper operation and monitoring during low power. The next-generation product with improved environmental performance, which can be used in microcars and B-class compact cars, will be mass-produced in 2017.
In January 2016, the company announced the development of “Active on Centering Control,” an electric power steering (EPS) technology that improves comfort when turning the steering wheel back to the straight-ahead state. The control can correct the most suitable steering angle and reduce the burden on the driver when turning the steering wheel. If the steering angle sensor is installed, special parts, etc., are no longer required, and EPS control is all that is needed. As a new technology to reduce costs and improve comfort, it is expected to be practical after 2017.
Steering system structural component suppliers
- ECU: Since we do not manufacture our own, we use electronic components from Denso, Hitachi Automotive Systems, Nidec Elesys, Omron, Mitsubishi Electric, and other suppliers as required by the vehicle manufacturers.
- Motors: We use the products of motor and electronic component suppliers such as Nidec, Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi Automotive Systems, and Mitsuba.
3) Hitachi Automotive Systems
The power steering business of Hitachi Group was merged with the power steering business of Unisia Jecs and Bosch Braking Systems (formerly Automotive Equipment Corporation) in 2001 to form Unisia JKC Steering Systems, which was unified into the Automotive Equipment Division of Hitachi, Ltd. in 2008. In 2009, Hitachi Automotive Systems was separated from Hitachi and became a subsidiary.
In 2009, Hitachi Automotive Systems became a subsidiary of Hitachi, Ltd. and became the third-largest power steering company in Japan after NSK Steering Systems, with a share of more than 10%. (Domestic share of EPS 6.6% and HPS 26.1% in 2014)
Like JETAG, which has the highest share, the company produces three types of steering systems: conventional hydraulic (HPS), electrohydraulic (EHPS), and electric power steering (EPS), and the proportion of domestic sales of hydraulic power steering is higher than that of electric power steering, which dominates the Japanese market. The reason is that the company supplies hydraulic power steering to Nissan, Mazda, Mitsubishi and other vehicle manufacturers, but only supplies electric power steering to Fuji Heavy Industries and Mitsubishi, and plans to expand sales of electric power steering to other vehicle manufacturers as well.
The characteristics of the company’s EHPS are that only the motor generates hydraulic pressure when steering, resulting in less energy loss. The product, jointly developed with Nissan, is called the “electro-hydraulic electronically controlled power steering system” by Nissan. The new EHPS is equipped with Nissan’s hybrid cars “FUGA” and “CIMA”.
Fuji Heavy Industries and Hitachi, Ltd. jointly developed the driver assistance system “EyeSight” to develop new functions, and the Subaru Levorg, which will be launched in 2014, is equipped with “EyeSight Ver.3” that can be coordinated with electric power steering (steering operation). The “EyeSight Ver. 3” on the Subaru Levorg, which was launched in 2014, can coordinate with the electric power steering system (steering assist and reverse control) to achieve active lane keeping and lane departure control, and is standard on all Levorg models except the low-cost versions. Subaru has announced that in 2017 it will release a quasi-autonomous driving car equipped with the “EyeSight” upgrade, which will make it possible to perform actual autonomous driving on the same lane of a dedicated road. Although its official name has not yet been announced, it is widely believed to be “EyeSight Ver.4”.
Steering system structural component suppliers
- ECU: In addition to in-house production, Denso and other electronic component suppliers are used.
- Electric motors: In addition to in-house production, products of electric motor and electronic component suppliers such as Mitsuba are used.
- Hydraulic pumps: In addition to in-house production, products from KYB and other hydraulic component suppliers are used.
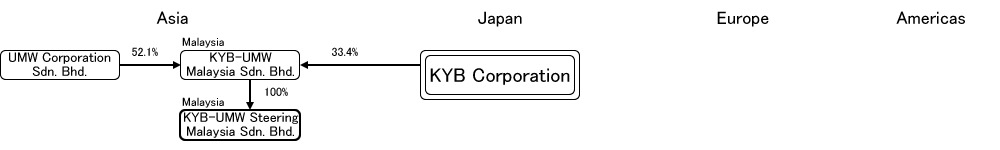
3) KYB
KYB was officially renamed KYB Corporation on October 1, 2015.
KYB holds the fourth largest share of the power steering market in Japan, after Hitachi Automotive Systems, with a share of about 3%. It is a large and established supplier of hydraulic components such as shock absorbers. (Domestic share EPS 0.7%, HPS 29.2% in 2014)
In addition to domestic production of HPS, we also have production plants in Thailand and Spain, and supply our products worldwide. On the other hand, as the market trend toward EPS replacement is growing rapidly, it is expected that the demand for hydraulic pumps for HPS will decrease, and the development and production of EPS will become a priority.
As with Hitachi Automotive Systems, the proportion of domestic sales of hydraulic power steering is higher than that of electric power steering. However, in 2013, we started our own production of ECUs and took the opportunity to expand from Mazda, Mitsubishi and Fuji Heavy Industries to sell electric power steering to Nissan.
We also supply EPS for ATVs and UTVs for motorcycles and EPS for racing cars. We also produce products related to electric rear wheel steering.
In April 2012, we established the Electronics Technology Center (Sagamihara City, Kanagawa), which focuses on the development of EPS systems such as ECUs, sensors, and circuits, and we have increased the number of engineers specialized in EPS to improve our development capabilities. We hope to strengthen our EPS development capabilities and develop them into a profit pillar for the automotive division as soon as possible, second only to the shock absorber business. When developing the next generation of EPS, the term “EV response” and “steer-by-wire” are often mentioned.
The new steer-by-wire technology, developed in collaboration with Nissan, communicates steering signals through an electronic harness and is the first in the world to be fitted to a production vehicle, and was installed in the Skyline hybrid of the V37, which went on sale in February 2014. Nissan named the new technology “DAS Active Steering by Wire” as a major technical selling point for this model. The new technology converts the steering action into an electronic signal through three ECUs and communicates it to the steering angle actuator, enabling fast steering operation without excess reaction force and easy driving. Together with the ALC active lane control technology and other driver assistance systems installed in this model, this technology will be an important technology for future autonomous driving.
In July 2015, Cadillac announced that it had begun researching technologies to integrate steering and shock absorber control. Based on the steer-by-wire technology, which is the first mass-produced technology in the world for some Nissan and other vehicles, the steer-by-wire technology can be used in conjunction with electronically controlled shock absorbers to improve driving safety and comfort. This technology is necessary for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and future autonomous driving, and Calyon will promote research to make it practical.
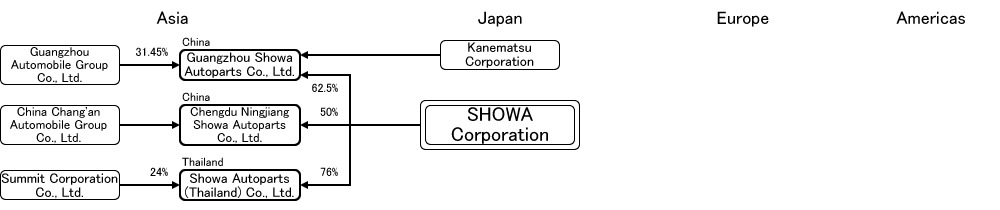
4) Sho-wa
Honda is a major parts supplier and Honda is the largest shareholder. Its main products are chassis components such as shock absorbers and electric power steering systems for motorcycles and automobiles, and its EPS business began with the transfer of Honda’s development and production operations. The first product produced by Showa was the rack-assisted coaxial EPS, which was installed in the 97M Accord. Later, the gear-assisted type was added to the product lineup, and both types are currently being produced. The hydraulic type used to be produced, but since it was discontinued, all of the current models are electric, except for its replacement. As for the development of C-EPS, Showa announced in its announcement on March 30, 2012 that it has started to explore a strategic business partnership with Trina, which will result in Trina developing C-EPS and Sho-wa developing DP-EPS.
The company ranks fifth in the Japanese power steering market after KYB, with a share of 1 to 2%. (Domestic share of EPS 2.1% and HPS 1.7% in 2014) Since we do not produce C-EPS for small cars, we are not able to supply Honda’s N series minivans and Fit and other small cars, which is one of the reasons for Showa’s low share of power steering.
In May 2015, we started production of the newly developed Dual Gear Power Steering System (DP-EPS) at the Gotenba Plant. . The system is the first to be used in Mazda’s new “ROADSTER” model, achieving improved operating comfort and high power output. The power steering equipment is located away from the steering section so that the steering operation is more comfortable. The installation of a reduction device on a separate part of the steering shaft makes it possible to optimize the reduction ratio and increase output power efficiently. After the ROADSTER, the product will be produced at the Gotemba Plant and exported to Honda’s Civic TYPE-R, which will be produced in the UK. Showa has also received global orders for DP-EPS for the next phase of Honda’s 16M Civic and 17M CR-V, with orders from North America to be produced at the Mexico plant. In addition, Showa will increase production capacity at the Mexico plant to meet the expanding demand for EPS in the North American market, reaching an annual production capacity of 1 million units in 2018, twice the forecast for fiscal 2016.
5) TRW Automotive
TRW Automotive has a strong position in the field of safety technology-related components such as airbags, seat belts, steering systems, driver assistance systems, brakes, ABS, ESC, and electric parking systems. Currently, we are promoting the development of high-end driver assistance systems with the goal of semi-autonomous driving.
In our Japanese business, we have been producing steering-related parts such as gears and ball joints since 1970 and supplying them to Japanese vehicle manufacturers and parts suppliers. In the power steering business, we supply products to Mazda and Mitsubishi, which have global sales. (Domestic share EPS 1.4%, HPS 0% in 2014)
Like JTEKT and Hitachi Automotive Systems, we produce conventional hydraulic (HPS), electrohydraulic (EHPS), and electric power steering (EPS) systems. Electric power steering is produced in both column-assisted (C-EPS) and rack-assisted (R-EPS) versions. Among them, the rack-assisted EPS uses the belt drive method, through the combination of rack and belt drive, ball nut, to achieve rack power.
As mentioned above, in the Japanese market only Mazda, Mitsubishi, and other parts of the OEM supply products, in the global market for Volkswagen / Audi, Ford, Volvo, and other OEM support.
Production of electric power steering began in 2001, and as of 2014, more than 26 million units have been supplied worldwide.
The C-EPS for Mazda’s 6th generation (Mazda2 produced in Japan, Mexico, and Thailand), which went on sale in 2014, is produced centrally in China and supplied to Mazda globally. The C-EPS for the Mazda CX-3 (produced in Japan) is also produced in Trina China, and the EPS is produced in five plants in Poland, Spain, Slovakia, China, and Brazil.
In 2014, Trina will begin supplying the third generation of its ECU/motor/main structural components to the European and Chinese markets, modularizing the electric power steering system (EPS CD), with a planned annual production capacity of 1 million units. VW Polo/up!/e-up!, Audi S1, Skoda Rapid/Fabia/Citigo, and Fiat 500L and Viaggio (GAC Fiat), in that order.
We plan to strengthen business alliances with Japanese auto parts suppliers in Shinkoku through complementary plants and joint development of products. In particular, we will focus on Brazil, where production began later than in China and India, and we hope to expand our business in Japan by strengthening business relationships with Japanese suppliers.
The acquisition of Trina by ZF in Germany was approved at the general meeting of shareholders of Trina in the United States in November 2014. The acquisition was valued at $12.4 billion and is scheduled to be completed in the first half of 2015. Bosch acquired ZFLS, the steering division of ZF, and Bosch, a 50-50 joint venture.
6) Robert Bosch Automotive Steering GmbH (formerly ZF Lenksysteme GmbH)
On January 30, 2015, the Bosch Group acquired ZF Lenksysteme GmbH, a 50-50 joint venture with ZF Friedrichshafen AG, and transformed it into a wholly-owned subsidiary, Robert Bosch Automotive Steering GmbH.) Robert Bosch Automotive Steering GmbH supplies steering systems to the Bosch Group. (2014 Japanese domestic share EPS 0.3% (Honda Odyssey DP-EPS), HPS 0%)
EPS market plants are located in Europe, North America, China, India, Brazil, and Malaysia.
As of April 2016, Japanese OEMs’ commercial dealings in Japan included dual-gear power steering (DP-EPS) for the Honda Odyssey launched in November 2013 and rack power steering (R-EPS) for the Honda Legend launched in February 2015.
- Although not produced in Japan, the Honda 18M Accord is supplied with DP-EPS from Bosch’s North American and Chinese plants, respectively (Thailand is supplied from KD in North America).
7) Thyssenkrupp Presta AG
Thyssenkrupp is a German supplier of steel and industrial products, with a focus on steel, stainless steel, alloys, and other metal products, including automotive components, shipbuilding, elevators, and large bearings. The automotive steering business is carried out by Thyssenkrupp Presta AG, a subsidiary of Thyssenkrupp, with a product lineup that includes steering shaft and strut modules, power steering (electric and hydraulic), and more.
The company’s entry into the EPS market began with the BMW X3, which went on sale in 2010. Although a latecomer to the market, the company has expanded its range of products to include the BMW X3 and several D and E class vehicles from BMW and Daimler.
In 2013, only the R-EPS rack and pinion parallel type were mass-produced (the estimated number of units shipped in 2012 was about 450,000), but now the C-EPS has also joined the mass production.
The company is also actively developing cooperation with Japanese OEMs, for example, for Mazda’s 7th generation (Mazda3), which has a highly competitive production base in China and is likely to enter the Japanese market.
3 Global business status of major power steering component suppliers
1) Status of business development a global business bases
Production bases / R&D bases
| JTEKT | Nippon Seiko | KYB | Sho-wa | Hitachi Automotive Systems | Trina | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia & Oceania | ||||||
| Japan | Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
| China | Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases R&D Base |
| India | Production Bases | Production Bases | ||||
| Indonesia | Production Bases | |||||
| Malaysia | Production Bases | Production Bases | ||||
| Korea | ||||||
| Taiwan, China | Production Bases | |||||
| Thailand | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases | |
| Vietnam | ||||||
| America | ||||||
| Argentina | Production Bases | |||||
| Brazil | Production Bases | Production Bases | ||||
| Canada | Production Bases | |||||
| United States | Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases R&D Base |
Production Bases | |||
| Mexico | Production Bases | |||||
| Europe | ||||||
| Germany | ||||||
| Czech Republic | Production Bases | |||||
| France | Production Bases R&D Base |
|||||
| Poland | Production Bases | Production Bases | ||||
| Slovakia | Production Bases | |||||
| Spain | Production Bases | Production Bases | ||||
| United Kingdom | Production Bases | Production Bases | Production Bases |
Note: Only production bases for power steering components and power steering-related components are recorded.
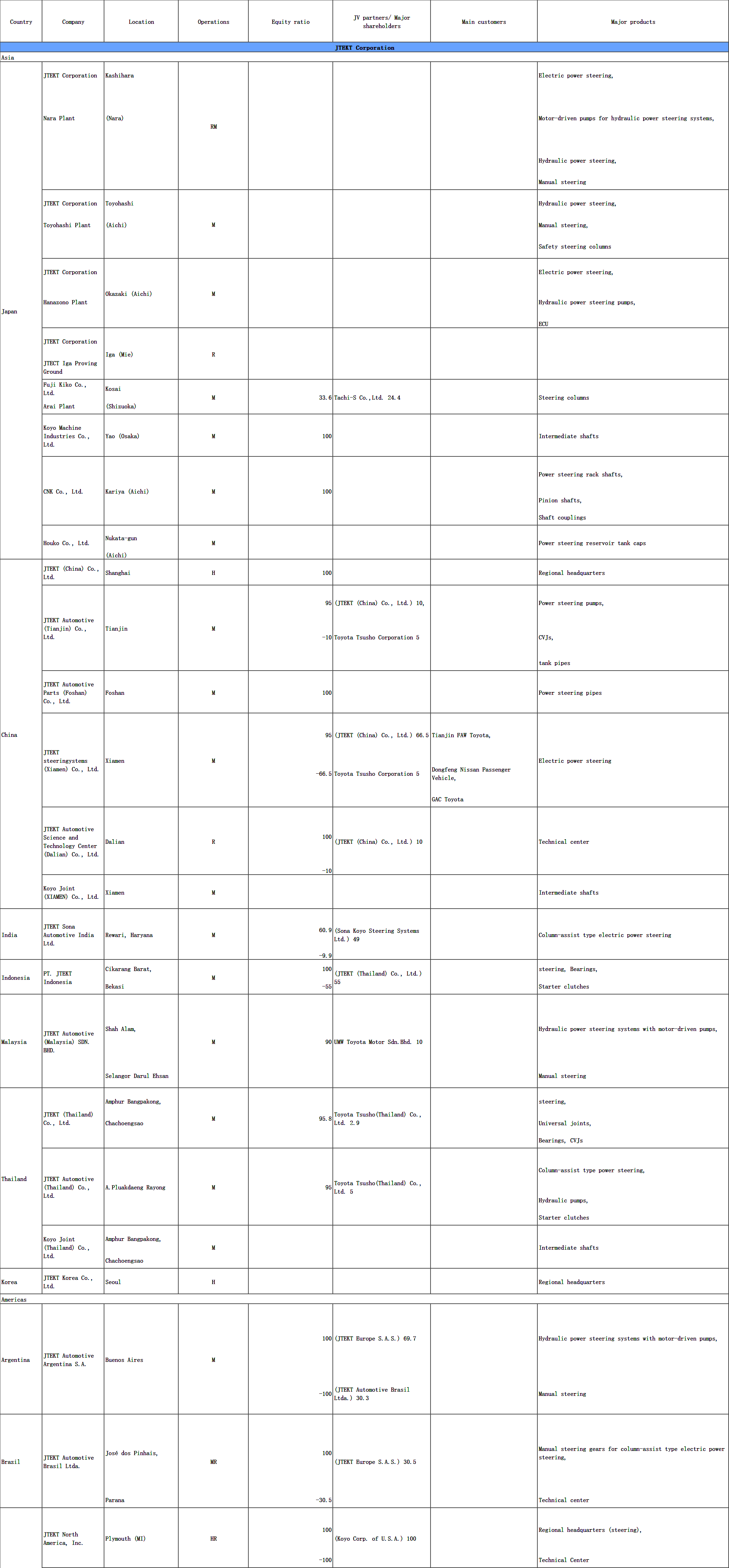
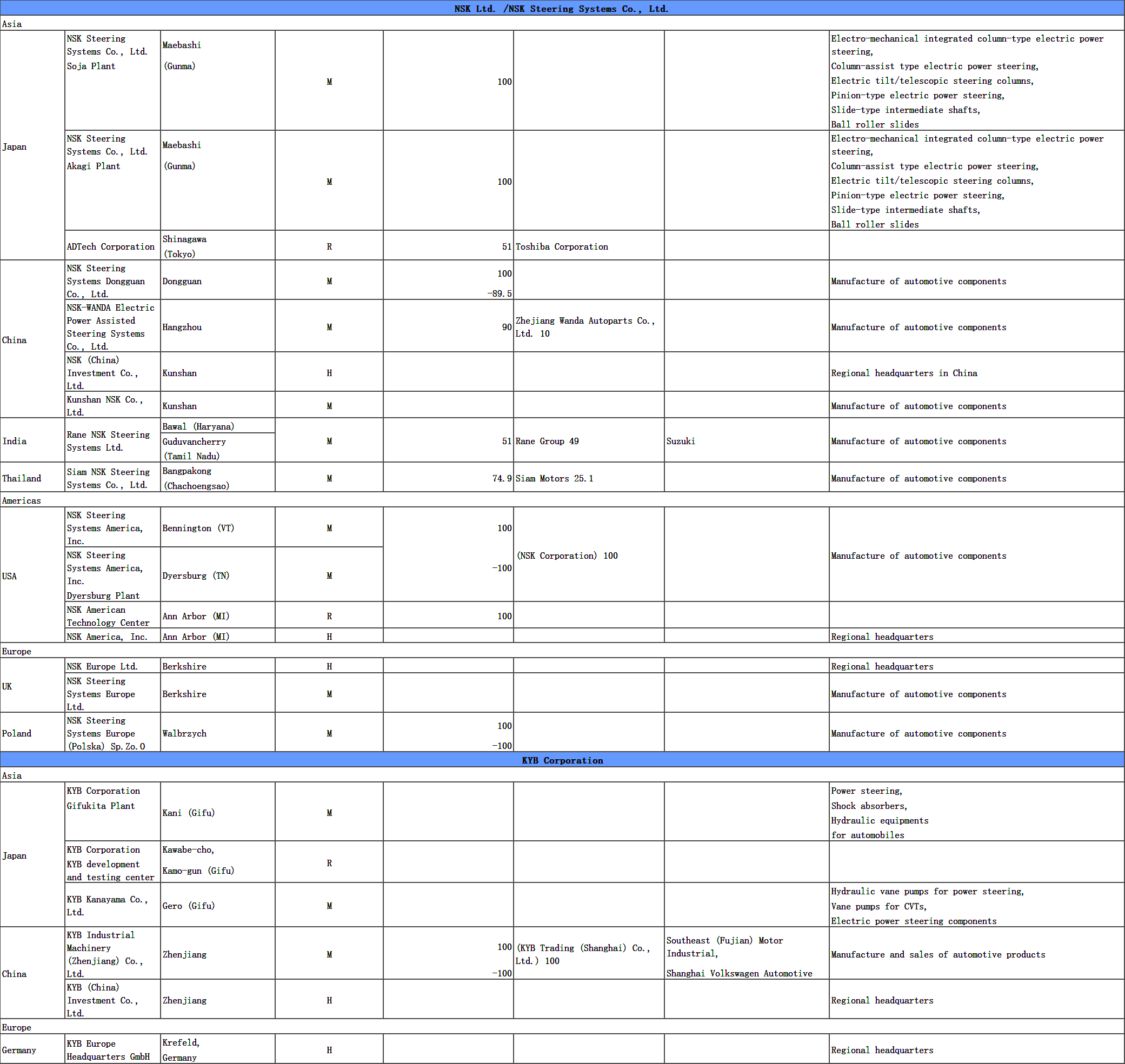
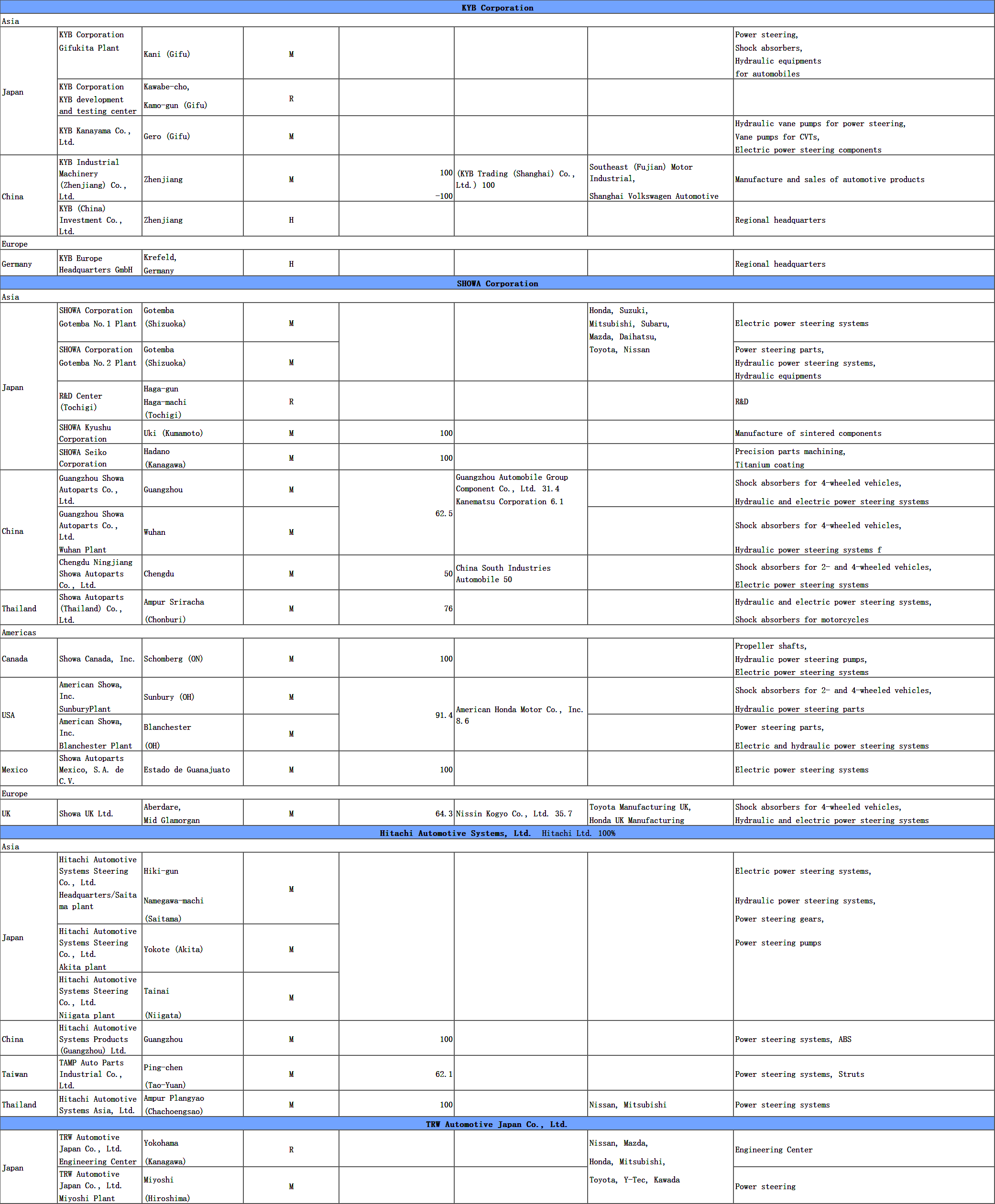
2) Status of business development at global sites (site name, address, major customers, etc.)
3) Map of major partnerships and joint ventures
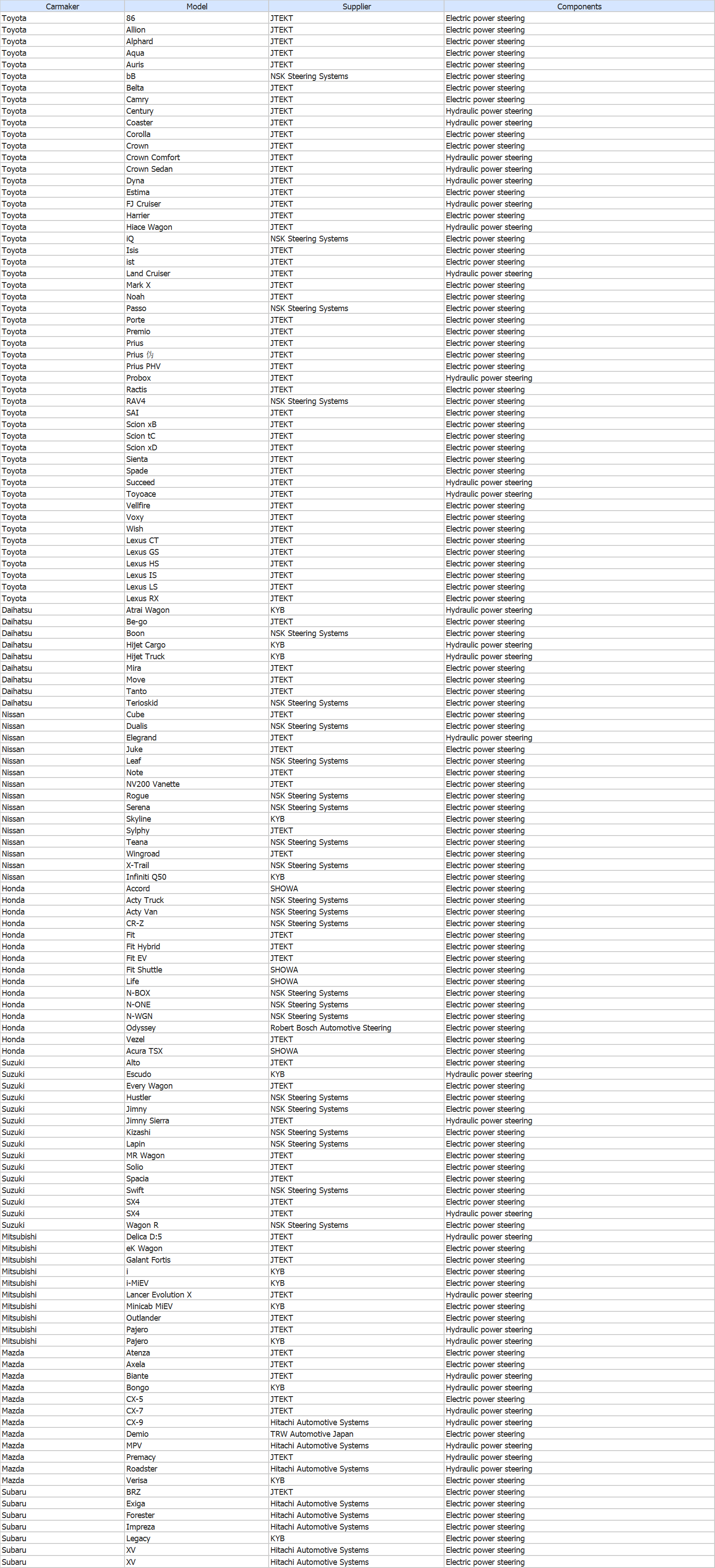
4 Major power steering component suppliers and OEM customers (Japanese production models)
Power steering (including other OEM’s labeled supply models)
| Toyota | Nissan | Honda | Mazda | Mitsubishi | Fuji Heavy Industries | Daihatsu | Suzuki | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JETAGAT | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| NSK Steering Systems | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Hitachi Automotive Systems | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| KYB | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Sho-wa | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Trina | ✓ | |||||||
| Robert Bosch | ✓ |
6 Status of business development in global business bases (Details)
H: Regional Headquarters /M: Manufacturing facility/ R: R&D and Technical center
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?








F*ckin’ tremendous things here. I am very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
I just could not leave your website prior to suggesting that I extremely loved the standard info a person provide in your visitors? Is gonna be back steadily to check out new posts
I love your writing style really enjoying this internet site.
Some genuinely wonderful blog posts on this web site, thanks for contribution.