The steering system is an important security subsystem for all kinds of cars, and the quality of its products directly affects the handling, comfort, and steering safety of the car, and plays an important role in reducing driving accidents and improving the driving experience of drivers.

Classification of power steering rack: hydraulic power, electro-hydraulic power, pure mechanical, electric power. Traditionally, power-hydraulic steering is widely used, but its structure is complicated, high energy consumption, frequent noise and oil leakage, and difficult to manufacture and assemble. In view of this, we have been looking for an optimal power-assisted way to meet better handling, less energy consumption, fast response, and more humane steering to adapt to different roads.
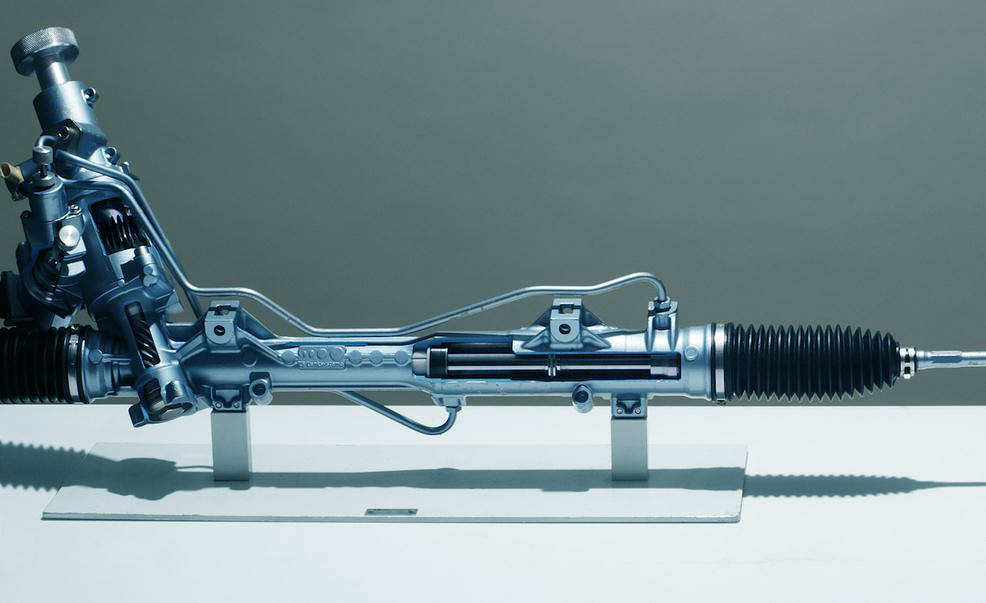
Electric Power Steering (EPS) was introduced in the early 1980s. Compared with the traditional steering, it has a simple structure, less number of parts, and more reliability. It eliminates the oil pump, pipeline, cylinder, and seal of the hydraulic steering, and only relies on the electric motor to assist through the control device, which solves the problems of oil leakage and low efficiency of the hydraulic steering.
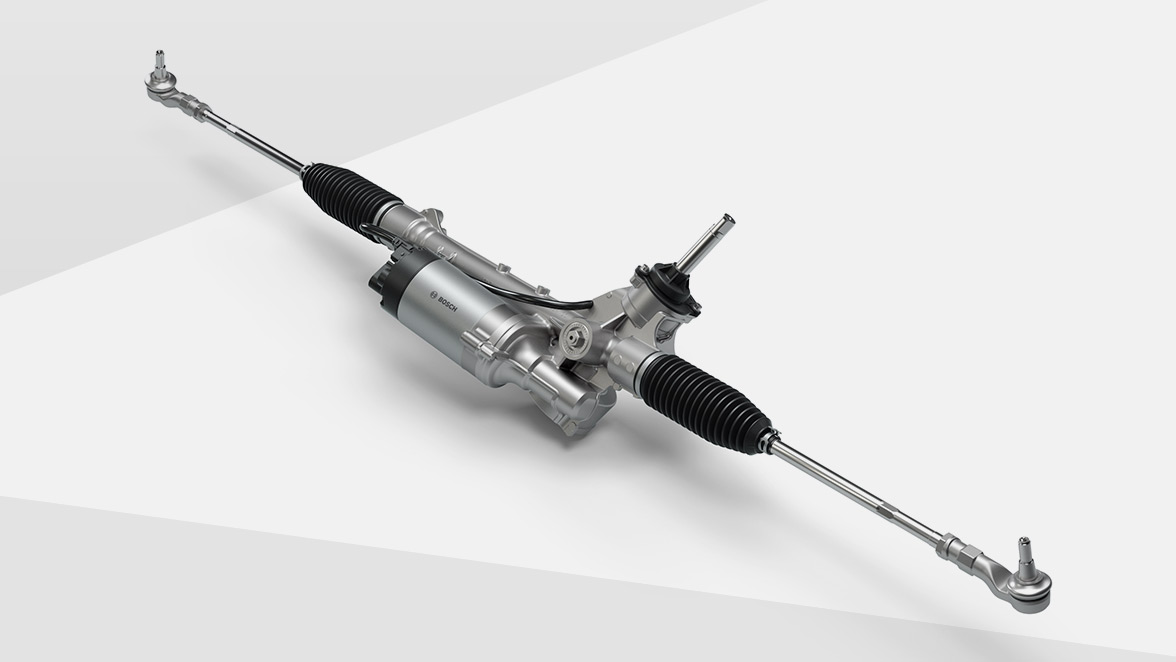
Electric power steering is developed on the basis of pure mechanical steering. Its power source is an electric motor, which distributes power for different roads and speeds through a control system (ECU). The electric power steering system consists of three main components: signal sensor (including torque sensor, angle sensor, and speed sensor), steering power mechanism (motor, clutch, reduction drive mechanism), and electronic controller. When the motor vehicle driver is driving through different driving environments, the speed signal gets feedback on the speed sensor, the steering wheel inputs the torque signal, and the motor distributes the power according to the different situations.
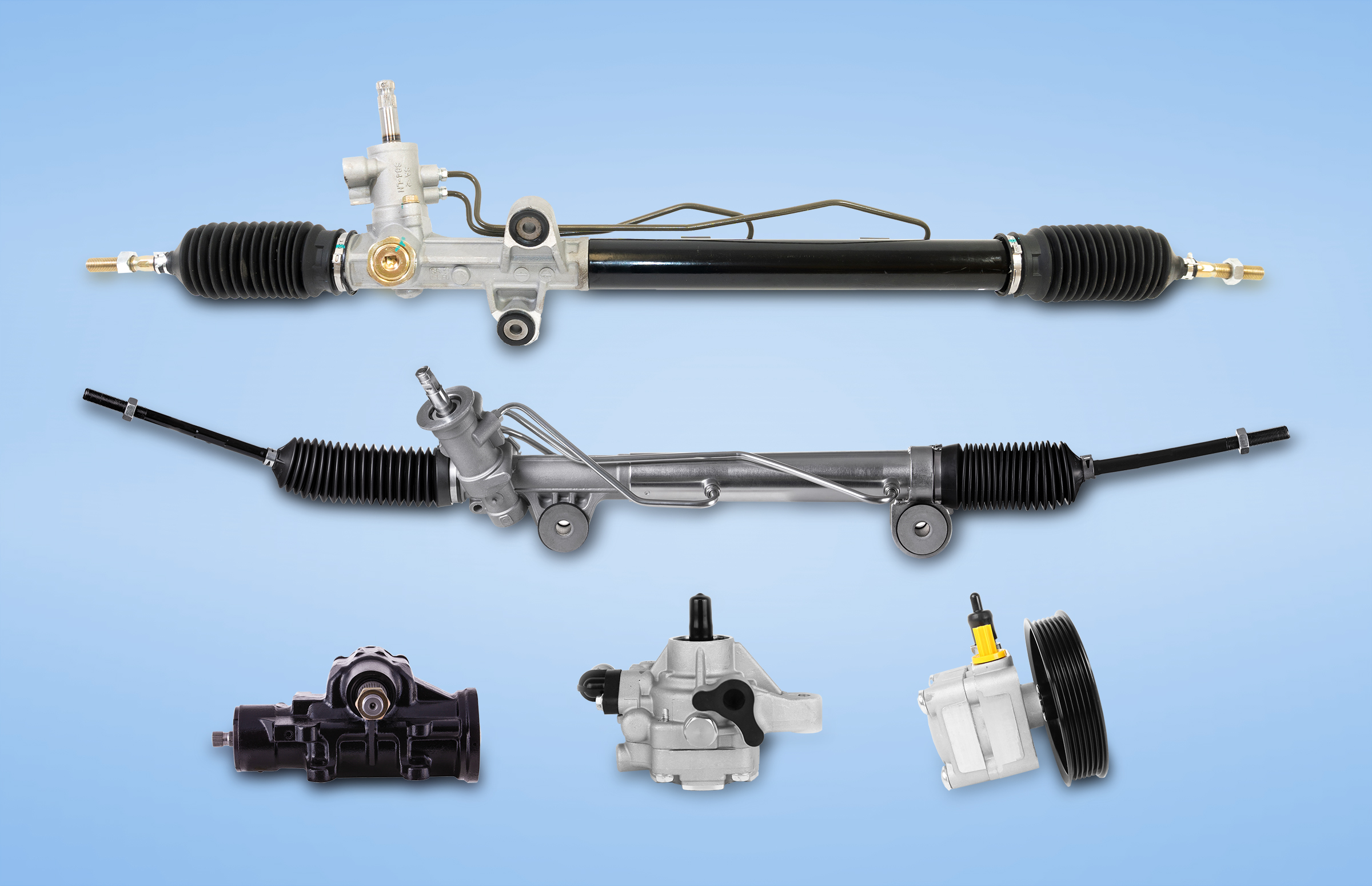

At the end of the 20th century, the automotive industry had 40 percent recirculating ball steering, 45 percent rack and pinion steering, 8 percent worm-roller steering, and 7 percent other types of steering. Recirculating ball steering gears have always occupied a place and are generally found on medium and large vehicles, which require a larger output torque and a heavier front axle load. Currently, rack and pinion steering gears are also being developed as the technology becomes more sophisticated, and more and more rack and pinion power steering gears are being used on medium-sized passenger cars and commercial vehicles.
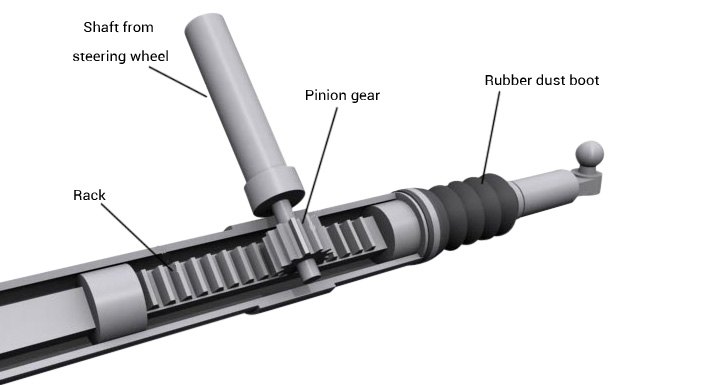
In Japan, various types of steering gear exist for different types of vehicles. Large buses and construction vehicles already use 100% of circulating ball type power steering gears, while cars increasingly use rack and pinion type steering gears, and electronic power-assisted rack and pinion type power steering gears account for an increasing proportion, accounting for 70%.
But in the world, the proportion of various types of the steering gear is also different, minibusses, for example, the United States and Japan use more circulating ball type steering gear, the use of more than 90%; while in Europe, the use of rack and pinion type more, the most use has reached more than 80%.
To sum up, in large engineering vehicles and buses, most of them use circulating ball type hydraulic power steering due to the high strength and power output required; in pickup trucks and small passenger cars, rack and pinion type hydraulic power steering is the mainstream; electric steering system will be the future trend in small passenger cars due to its low energy consumption and better operability, gradually replacing rack and pinion type hydraulic power steering.
(We do not share your data with anybody, and only use it for its intended purpose)
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?







Leave A Comment