According to the data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, in 2014, China produced 23,722,900 vehicles, up 7.3% year-on-year, and sold 23,491,900 vehicles, up 6.9% year-on-year, maintaining the world's top production and sales volume.
The huge automobile production and sales volume have a large demand for automobile steering rack grease, so the development of China's automobile steering rack grease is of practical significance.

1 Type of automotive steering racks
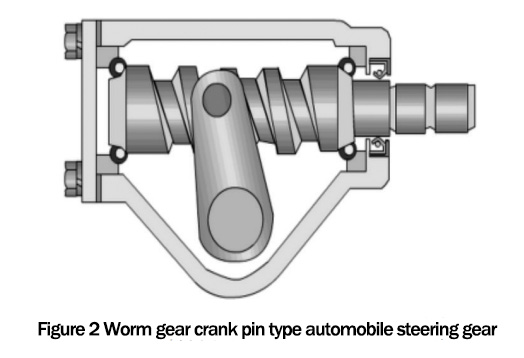
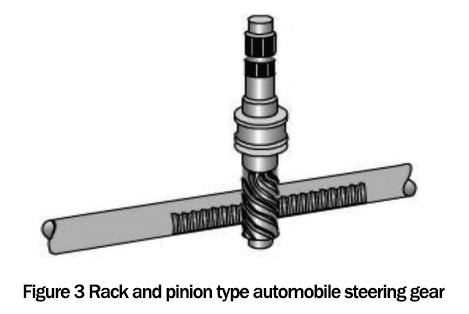
Commonly used automotive steering gears like 44200-0K040 include recirculating ball-type automotive steering gears, worm crank-pin, and rack-and-pinion steering gears. Their structures are shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3 in order.
The circulating ball-type automobile steering gear is equipped with a circulating steel ball between the screw and the nut. with circulating steel balls, so that sliding friction becomes rolling friction. This improves transmission efficiency. The advantages of this type of steering gear are light operation The disadvantage is that the structure is complicated, the cost is high, and the steering sensitivity is not as good as the rack and pinion type. The disadvantage is that the structure is complicated, the cost is higher, and the steering sensitivity is not as good as the rack and pinion type.
Worm gear crank pin type steering gear is a steering rack with worm gear as the active part and cranks pin as the follower, which is usually used for heavy trucks with high steering force.
The rack and pinion steering gear uses gear rotation to drive the rack to move left and right, and its structure is simple. The second is that when the steering power is needed, whether it is hydraulic or electric power, it is easy to be combined with the steering knuckle. The second is that when steering assistance is needed, it is easy to integrate with the steering gear, whether it is hydraulic or electric assistance. Therefore, rack and pinion steering gears are mainly used in passenger cars.
2 Requirements of grease for a rack and pinion steering gear
The working environment of the car is usually outdoors, encountering the environmental temperature difference The temperature in the north can be as low as -40 ℃ in winter, while the temperature in the south can reach over 70 ℃ in summer underexposure. In winter, the temperature in the north can be as low as -40 ℃, while in summer, the temperature in the south can reach over 70 ℃ under the sun. Therefore, it is required that the rack and pinion steering grease should have good high and low-temperature performance; in order to prevent the base oil of rack and pinion steering grease from to prevent the loss of base oil and lubricating performance under the high temperature of rack and pinion steering grease, it is required that grease should be small and have good colloidal stability; in order to ensure the long-term lubrication of the steering gear, it is required In order to ensure the long-term lubrication of the steering gear, the grease of rack and pinion car steering gear should have excellent anti-oxidation property. In order to ensure the long-term lubrication of the steering gear, the grease should have excellent anti-oxidation properties. Therefore, it is required that the rack and pinion steering grease should have good lubricity. grease should have good lubricating performance and anti-wear performance; at the same time, it should have Therefore, the grease should have good lubricating performance and anti-wear performance; meanwhile, it should have good protection performance for metal; and good compatibility with the sealing sleeve.
According to the performance requirements of rack and pinion steering grease, and with reference to a famous foreign brand of gear and with reference to the performance of a famous foreign brand rack and pinion steering grease. The technical indexes of the proposed rack and pinion automotive steering rack grease are as follows The technical indexes of the proposed rack-and-pinion grease are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Technical indexes of the proposed rack and pinion type automobile steering rack grease
| Projects | Technical specifications | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Working cone entry degree (* 25 ℃)/unit | 310~340 | GB/T269 |
| Non-working micro cone entry (* -40 °C) / unit | ≥46 | GB/T269 |
| Similar viscosity (-40 °C, 10 s⁻¹) ) (/ Pa⁻s) | ≤1800 | SH/T0048 |
| T₂ copper sheet corrosion (100 ℃, 24 h) | No green or black change | GB/T7326 B method |
| Oxidation pressure drop (99 ℃, 100 h)/kPa | ≤20.0 | SH/T0325 |
| Titration point/°C | ≥190 | GB/T4929 |
| Stencil oil separation (100 ℃, 24 h), % | ≤5.8 | SH/T0324 |
| Evaporation loss (99 ℃, 22 h), % | ≤0.25 | GB/T7325 |
| Max. non-snagging load/N | ≥1000 | SH/T0202 |
| Sintering load/N | ≥1960 | SH/T0202 |
Note: * Both taper-in and micro-taper-in are in 0.1 mm, same as below.
From the technical indexes set in Table 1, the operating temperature of the proposed rack and pinion steering rack grease is -40 ℃~150 ℃.
3 Development of rack and pinion steering rack grease
(1) Base oil design
The base oil of the proposed rack and pinion automotive steering grease is mainly designed from two aspects, one is to consider the low-temperature working condition of the steering gear grease; the other is to consider the greasing performance and cost of the base oil. Therefore, the API II base oil with high viscosity index and poly alpha-olefin (PAOs) with excellent low-temperature performance were blended to obtain the blending base oil, and the 40 ℃ kinematic viscosity of the blending base oil was controlled between 61.2 mm²/s and 74.8 mm²/s according to the practical experience, and its typical physicochemical data are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Typical physicochemical data of blending base oils
| Projects | Typical Data |
|---|---|
| 40 ℃ kinematic viscosity(/ mm² *s⁻¹ ) | 65.45 |
| Viscosity index | 101 |
| Pour point/°C | -35 |
This blending base oil is cost-effective and can meet the low-temperature performance requirements of rack and pinion steering gear grease.
(2) The choice of thickening agent
Lithium 12-hydroxy stearate soap grease has excellent mechanical stability, a long life cycle, also has good water resistance, and can adapt to the car due to climate or geographic location changes brought about by the wet environment; at the same time, the thickening ability of lithium 12-hydroxy stearate soap is strong, so the choice of lithium 12-hydroxy stearate soap as the thickening agent for the proposed development of steering grease. The typical data of the base grease obtained by thickening and blending the base oil (refined mineral oil with high viscosity index + PAOs) with lithium 12-hydroxy stearate soap are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Typical data of basic grease
| Projects | Typical Data |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White uniform oil paste |
| Working cone entry degree (25 ℃)/unit | 315 |
| Not working micro cone entry (-40 ℃) / unit | 50 |
| Titration point/°C | 201 |
| Stencil oil separation (100 ℃, 24 h), % | 4.0 |
| Similar viscosity (-40 °C, 10 s⁻¹) ) (/ Pa⁻s) | 1212 |
As seen in Table 3, the high and low-temperature performance of the prepared base grease performance is good, which indicates that the selection of thickener and base oil system is reasonable.
(3) Examination of additives
(3.1) Anti-wear and extreme pressure agents
The speed of rack and pinion car steering is low, and the friction condition is bad, mainly sliding friction, so the anti-wear and extreme pressure performance of the rack and pinion car steering grease is required to be high, for this reason, the compounding of several anti-wear and extreme pressure agents was investigated, see Table 4.
Table 4 Examination of anti-wear extreme pressure agents
| Projects | 0.5% sulfur-containing agent + 1.0% phosphorus-containing agent + 1.0% molybdenum compound | 1.0% molybdenum compound + 1.0% zinc salt | 1.0% phosphorus containing agent + 0.5% molybdenum compound + 1.0% zinc salt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering load/N | 1960 | 1960 | 1960 |
| Abrasion/mm | 0.363 | 0.357 | 0.332 |
Note: Abrasion test conditions 392 N, 1200 r/min, 5 min.
From the examination of Table 4, we can see that the 2.5% mass fraction of the compound anti-wear polarizing agent (1.0% phosphorus-containing agent + 0.5% molybdenum compound + 1.0% zinc salt) has smaller wear traces and better anti-wear performance, which can be used as a compound anti-wear polarizing agent in rack and pinion type automobile steering rack grease.
(3.2) Antioxidant and metal deactivator
In order to extend the service life of the car steering grease, improve the antioxidant performance of the car steering grease, in the rack and pinion car steering grease with the right amount of antioxidants and metal deactivator. The antioxidant acts as an antioxidant and the metal deactivator can reduce the catalytic oxidation activity of the metal and play the role of an auxiliary antioxidant. The antioxidants and thiadiazole derivatives metal deactivators are examined in Table 5.
Table 5 Examination of antioxidants and metal deactivators
| Projects | 2.0% phenol antioxidant + 0.1% thiadiazole derivative | 2.0% amine antioxidant | 2.0% amine antioxidant + 0.1% thiadiazole derivative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidation pressure drop (99 ℃, 100 h)/kPa | 30.0 | 23.6 | 15.0 |
From the examination of Table 5, it can be seen that the oxidation pressure drop of 15.0 kPa with the addition of 2.0% amine antioxidant and 0.1% thiadiazole derivative metal deactivator has a good antioxidant performance and meets the requirements of the development index.
(3.3) Rust inhibitor
Automobiles are often driven in high temperature and humid environments, and the steering gear may be affected by the high temperature and humid environment and rust, so there are certain requirements for the rust prevention performance of the proposed rack and pinion type automobile steering rack grease. EMCOR bearing rust prevention test (distilled water) was used to The antirust performance of several antirust agents was investigated using EMCOR bearing antirust test (distilled water), and the results are shown in Table 6.
Table 6 Examination of antirust agents
| Projects | 1.0% carboxylate antirust agent | 1.0% sulfonate antirust agent | 1.0% organic amine rust inhibitor | 0.2% organic ester + 0.8% azepine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMCOR antirust test (distilled water)/grade | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
From the examination of Table 6, it can be seen that the effects of several rust inhibitors all reached the rust-free grade 0, and all of them can meet the requirements of the proposed rack and pinion type automobile steering grease requirements for rust prevention performance. Comprehensive consideration Consideration, the rust inhibitor of 0.2% organic ester + 0.8% nitrogen heterocyclic compound was chosen The compound rust inhibitor of 1.0% was compounded.
(3.4) Composition and Preparation
Through the above investigation, the composition of the rack and pinion automotive steering grease was obtained, which is composed of blending base oil (refined mineral oil with high viscosity index + PAOs, kinematic viscosity 61.2 mm2/s~74.8 mm2/s at 40 ℃), lithium 12-hydroxystearate soap thickener, 2.5% compound anti-wear extreme pressure agent (1.0% phosphorus containing agent + 0.5% molybdenum compound + 1.0% zinc salt ), 2.0% amine antioxidant, 0.1% thiadiazole derivative metal deactivator and 1.0% compound rust inhibitor (0.2% organic ester + 0.8% azomethine compound).
Add part of the blending base oil in the atmospheric pressure reactor, raise the temperature to 75 ℃ and add 12-hydroxystearic acid and lithium hydroxide aqueous solution for saponification reaction, and then raise the temperature to 210 ℃ for refining; after refining, add the remaining blending base oil and add additives at 80 ℃, and homogenize to obtain the finished rack and pinion type automotive steering rack grease.
4 Properties of rack and pinion steering rack grease
(1) Physicochemical properties
The physicochemical properties of the developed rack and pinion automotive steering grease (referred to as the developed steering grease) were evaluated and compared with the physicochemical properties of a well-known foreign brand of rack and pinion automotive steering grease (referred to as the imported steering grease), as shown in Table 7.
Table 7 Evaluation of physical and chemical properties of the developed steering rack grease and comparison with imported steering rack grease
| Projects | Grinding of steering rack grease | Imported steering rack grease |
|---|---|---|
| Working cone entry degree (25 ℃)/unit | 320 | 318 |
| Not working micro cone entry (-40 ℃) / unit | 48 | 46 |
| Similar viscosity (-40 °C, 10 s⁻¹) /(Pa*s) | 1257 | 1796 |
| T₂ copper sheet corrosion (100 ℃, 24 h) | No green or black change | No green or black change |
| Oxidation pressure drop (99 ℃, 100 h)/kPa | 15.0 | 10.0 |
| Titration point/°C | 193 | 202 |
| Stencil oil separation (100 ℃, 24 h), % | 5.0 | 5.8 |
| Evaporation loss (99 ℃, 22 h), % | 0.20 | 0.18 |
| Max. non-snagging load/N | 1019 | 1019 |
| Sintering load/N | 1961 | 1961 |
From the evaluation and comparison in Table 7, it can be seen that the developed rack and pinion automotive steering grease has reached the set technical index, and at the same time, it has comparable physicochemical properties with a well-known foreign brand of rack and pinion automotive steering rack grease and can be used in the temperature range of -40 ℃ to 150 ℃.
(2) Friction and wear performance
The friction condition of the automobile steering gear is bad, mainly sliding friction, which puts higher requirements on the friction and wears performance of rack and pinion automobile steering grease, so the friction and wear performance of the developed rack and pinion automobile steering grease was further investigated.
The friction condition of the car steering was simulated by a four-ball machine, and the friction and wear performance of the rack and pinion car steering grease under different temperatures, speeds, and the load was evaluated, and compared with the imported steering grease, see Table 8.
Table 8 Gear rack type automobile steering gear grease friction wear simulation test results
| Projects | Grinding of steering grease | Imported steering grease |
|---|---|---|
| Frictional wear performance at low temperature and low speed (40 °C, 92 r*min⁻¹, 392 N, 60 min) | ||
| Friction factor | 0.075 | 0.088 |
| Abrasion diameter/mm | 0.329 | 0.335 |
| Frictional wear performance at high temperature and high speed (75 °C, 1200 r*min⁻¹, 392 N, 60 min) | ||
| Friction factor | 0.041 | 0.072 |
| Abrasion diameter/mm | 0.369 | 0.374 |
| Frictional wear performance under 392 N load (30 °C, 1200 r*min⁻¹ for 10 min) | ||
| Friction factor | 0.048 | 0.060 |
| Abrasion diameter/mm | 0.343 | 0.333 |
| Frictional wear performance under 588 N load (30 °C, 1200 r*min⁻¹ for 10 min) | ||
| Friction factor | 0.064 | 0.051 |
| Abrasion diameter/mm | 0.379 | 0.387 |
| Frictional wear performance under 588 N load (30 °C, 1200 r*min⁻¹ for 10 min) | ||
| Friction factor | 0.069 | 0.054 |
| Abrasion diameter/mm | 0.437 | 0.435 |
From the simulation test in Table 8, we can see that the friction and wear performance of the developed rack and pinion automotive steering grease is comparable to or slightly better than the anti-wear and friction reduction performance of the imported steering grease under different temperatures, speed, and load.
(3) Service Performance
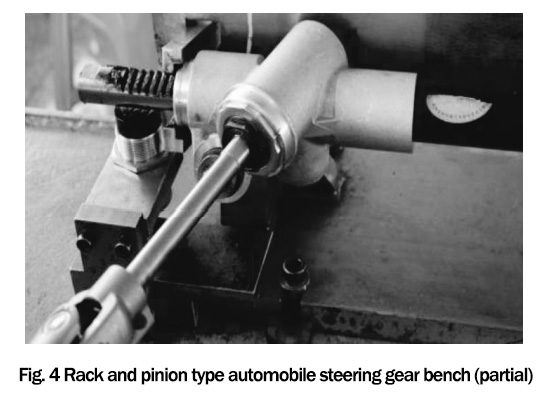
The rack and pinion steering grease bench test is an important method to evaluate the use performance of rack and pinion steering grease, and the rack and pinion steering grease bench is shown in Figure 4.
The rack and pinion car bogie have a rack tooth count of 30, a contact count of 22, a rack length (friction area) of 177 mm, a tooth height of 4 mm, a single tooth contact length of 3 mm, a tooth top width of 18 mm, and a contact width of 18 mm; the number of teeth of the gear is 8; the angle of intersection between the gear shaft and the rack is 70°; the friction time of the rack is 6.125 s on one side and one way; the rack runs at a speed of 28.90 mm/s The total length of 100,000 rubs per unit area (1 mm²) is 100 m; the friction speed per unit area (1 mm²) is 30.74 mm/s; the total time of 100,000 rubs per unit area (1 mm²) is 3253 s.
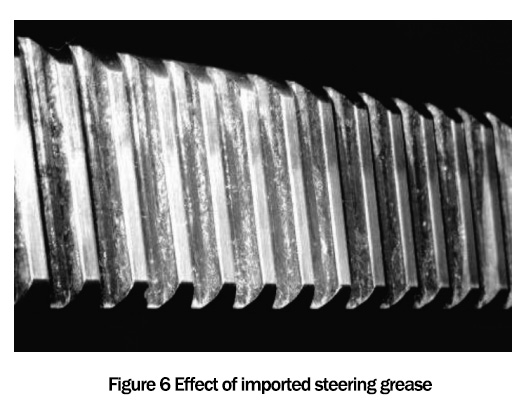
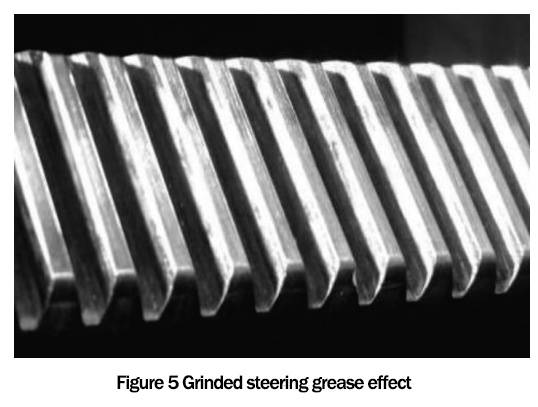
The results are shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6, respectively, from the 100,000-times bench test of the developed steering grease and the imported steering grease on the rack-and-pinion steering gear bench of a domestic automobile steering company.
Comparing Fig. 5 and Fig. 6, we can see that after the bench test, the rack of the developed steering grease is still brighter than the imported steering grease. The rack of the developed steering grease is still bright and slightly better than the imported steering grease. This shows that the performance of the developed steering grease is comparable to or slightly better than that of the imported steering grease. This indicates that the performance of the developed steering grease is comparable to or slightly better than that of the imported steering grease.
5 Conclusion
(1) The base oil was thickened with lithium 12-hydroxy stearate soap (refined mineral oil with high viscosity index + PAOs, kinematic viscosity 61.2 mm2/s~74.8 mm2/s at 40 ℃) and added with 2.5% compound anti-wear and extreme pressure agent (1.0% phosphorus-containing agent + 0.5% molybdenum compound + 1.0% zinc salt), 2.0% amine antioxidant, 0.1% thiadiazole derivative The rack and pinion automotive steering grease developed with 2.0% amine antioxidant, 0.1% thiadiazole derivative and 1.0% rust inhibitor (0.2% organic ester + 0.8% azocyclic compound) achieves the set technical indexes and its physical and chemical properties are comparable to those of imported rack and pinion automotive steering grease.
(2) The simulation test and bench test show that the developed rack and pinion type automobile steering grease has good friction and wear performance and use performance, and the friction and wear performance and use performance of imported rack and pinion type automobile steering grease are comparable or slightly better, and can be used in the temperature range of -40 ℃~150 ℃, and can meet the requirements of rack and pinion type automobile steering grease. It can meet the lubrication requirements of rack and pinion steering gear.
References
[1] Taking advantage of the best development opportunity to lead a new era of independent brands [J]. China Economic Weekly. 2015(09)
[2] Study on the synergistic anti-wear performance of phosphorus-containing friction modifiers[J]. Hu Jianqiang,Xie Feng,Hu Yingqin,Yao Junbing. Material Protection. 2006(08)
[3] Research progress on anti-wear and extreme pressure additives for lubricating grease[J]. Yao Junbing. Lubricants. 2006(03)
[4] Anti-wear and extreme pressure additives of thiadiazole derivatives in lubricating grease[J]. Yao Junbing,Wang Ruihua. Lubricants. 2005(02)
[5]Study on the compatibility of common friction sub-materials with anti-wear additives[J]. ZHOU Chunhong,DONG Junxiu,WEN Shichu,JIN Wonsheng. Journal of Tribology. 1992(01)
(We do not share your data with anybody, and only use it for its intended purpose)
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?








Leave A Comment