Oil coolers are heat exchangers to maintain a consistent operating temperature for lubricating oil in internal combustion engines, gearboxes, and other mechanical systems. To operate, they channel hot oil through tubes filled with a cooling medium like air or water, which then releases the heat into the surrounding environment. Oil coolers are used to lower the temperature of the oil to avoid damage to the engine and gearbox from occurring at high temperatures. Hence, it is undoubtedly important that you know about coolers and how you can manage them with your mechanical systems. This article will tell you about Oil Coolers.
1 What Is Oil Cooler?
An oil cooler keeps the oil supply at the ideal temperature, separate from the main radiator in an engine. Its function is to reduce the temperature of the oil flowing through the coils, thus extending the engine's service life and transmission. They sit in front of the radiator of a vehicle's engine: diesel engines (which operate at a higher temperature range) and an automatic transmission oil cooler. A vehicle's smooth operation relies on the cooler's ability to dissipate heat while also transferring oil away from moving parts and into the pan.
Adding an oil cooler to an air-cooled engine is an auxiliary cooling oil system, significantly lowering the temperature. There will be a significant improvement in the engine's lifespan. Oil coolers are useful for heavier trucks because they enable the drive train to endure greater stress.
The risk of a breakdown is mitigated, and engine oil temperatures are maintained thanks to the improved cooling efficiency. Oil loses its lubricating and cooling properties as it degrades.

2 What Are The Types Of Oil Coolers?
There are two primary kinds of oil coolers for engines: those that transfer the heat from the oil to water or air.
Oil-To-Water
Oil-to-water coolers have a heat exchanger that transfers heat from the oil to the water. Bringing warm oil up to temperature or cooling down too much oil makes the coolant work. In addition, as the cooling medium, these coolers use a liquid, such as water or a coolant. Liquid-cooled oil coolers are more common in large, demanding applications like those found in maritime and industrial settings because they are more efficient than air-cooled coolers.
Oil-To-Air
An oil-to-air cooler is a small radiator that transfers heat from the engine oil to the surrounding air. Most oil-to-air coolers have a thermostatically-controlled bypass valve that closes when the engine oil has reached the proper operating temperature. Moreover, Air is used as the cooling medium in these coolers, often used in less demanding yet smaller applications. Although inexpensive and easy to manufacture, air-cooled oil coolers are less effective than liquid-cooled coolers, especially in warm areas.
A common cooler is the tube-and-fin design, in which the oil is cooled as it travels through one or more devices. Some variants may use stacked plates or have more than one cooling row. Header-style oil coolers have end tanks that resemble radiators.
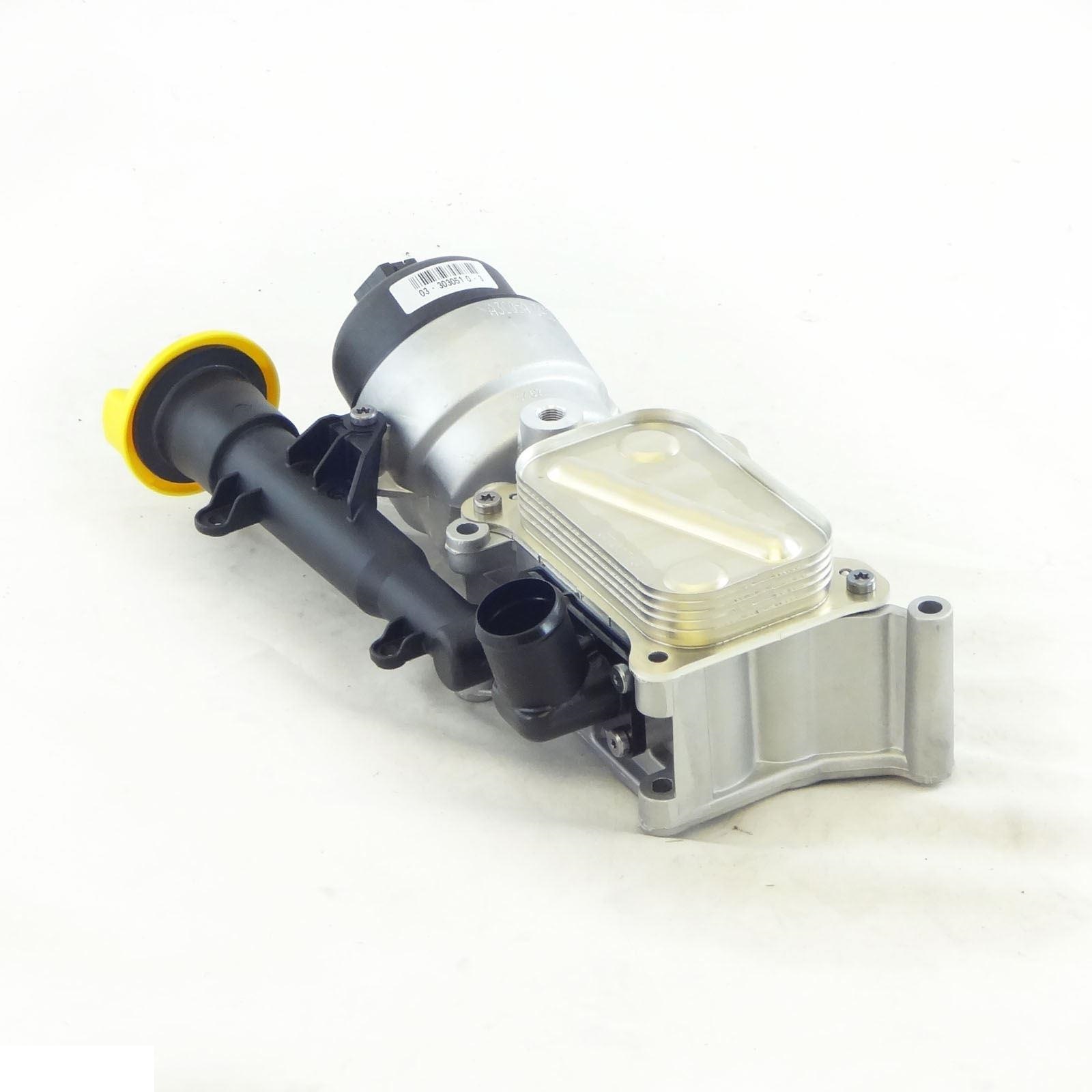

3 What Is The Function Of an Oil Cooler?
In oil-to-air coolers' operation, they are typically positioned at the front side of the radiator, although having the same shape. This expedites the engine oil's access to the cooling fan's coldest, freshest air. In most instances, the oil leaves the engine through a "sandwich" adaptor.
An adapter is installed in the oil filter's oil supply line and the engine block to facilitate the passage of hot oil through the filter. Back at the engine, it undergoes the same procedure after going through the oil cooler. When the oil within reaches a certain temperature, the thermostatic control on some sandwich adaptors will allow it to flow again.
It is possible to reuse the oil filter on your vehicle with the help of an adapter that is included in the design of some systems to connect the oil filter to the cooler and the far-off filter base.
4 Why Is It That Vehicles Need Oil Coolers?
Even though oil coolers are available for all vehicles, they are typically required for big automobiles.
For instance, if you tow a trailer going up for extended lengths, your engine will likely operate at high capacity for an extended amount of time. This generates a great deal of high temperature which must be dissipated. If heat cannot escape, it accumulates and increases the temperature of the engine. A cooler for oil gives additional surface area for this heat to evaporate.

5 How To Choose An Oil Cooler
There are various types and sizes of an engine cooler. This section will teach you the six key factors when selecting an oil cooler for your street rod.
●The capacity of oil in your engine's lubrication system
●The engine's output and the vehicle's intended purpose should be considered.
●Quantity of airflow required and available mounting space
●Radiator size
●Size of Inlets/Outlets
●Following your financial means
There are two main kinds of oil coolers: the tube and fin and plate or stacked plate. Both work the same way, but the plate or stacked plate type has a different design and more surface area. People usually call tube and fin coolers by how often the fluid or oil goes through the cooler's length before returning to the engine. With a two-pass cooler, the oil goes through the length of the cooler twice. The better a cooler is at moving heat, the more passes it has.
There is also the size of the inlet and outlet. Make sure you don't choose a size that is manageable and tight enough. If you do, the oil pressure will drop, which could damage the engine. Most engines use a port size of -8 AN or -10 AN, but some high-capacity/high-flow engines can also use a port size of -12 AN. You need a lot of oil to flow through the cooler for heat transfer.
Airflow through the cooling fins is the most important aspect of any engine oil cooler installation, regardless of whether it is created by the radiator's slipstream or a cooling fan. Also, remember that high airflow can cause the boundary layer to prevent air from reaching the cooling tubes and fins. You desire ambiance to flow over the fins and tubes to the point when heat is transferred to the atmosphere. If air moves too quickly across the tubes & fins, heat cannot escape and is trapped.
Furthermore, you should also need to learn about the qualities you might want to consider when choosing an oil cooler:
Temperature Reduction
The extent to which an oil cooler can transfer heat from the oil to the cooling medium is what establishes the cooler's cooling capacity. It's crucial to match the oil cooler's cooling capacity with the engine's or transmission's size and output.
Conditions Of Operation
An oil cooler's effectiveness is sensitive to operational circumstances like ambient temperature and humidity. When deciding on an oil cooler, it's important to consider the working circumstances to ensure it can handle the heat.
Cooling Medium Type
In addition to air, liquid can also be used as a cooling medium in oil coolers. Think about each cooling medium's efficiency, cost, and maintenance needs before deciding which one is best for your application.
Installation
It is crucial to select an oil cooler that is both sized appropriately for the task at hand and positioned in a position where it can achieve maximum cooling.
Longevity And Reliability
It is crucial to select a high-quality, long-lasting oil cooler built to endure the rigorous conditions of the intended use.
Expense
The price of the oil cooler should also be considered, as it will affect the system's total cost. Consider the expense of the cooler relative to the benefits it will give, such as increased engine or transmission life and increased economy.
Overall, it is essential to carefully analyze these criteria when selecting an oil cooler to ensure that it fulfills the application's requirements and limitations.

6 When You Should Repair Your Oil Coolers
A motor oil cooler should endure for many years with minimal issues. Cracks and leaks in the cooler are some of the most prevalent issues. Leaks are frequently caused by rust, but road vibrations can also be a factor, especially when driving off-road. Typically, this issue is more prevalent in older vehicles.
Either the coolant seeps into the oil, or the oil leaks into the coolant. This may lead to oil in the combustion chamber or an enlarged radiator. If you don't discover this issue early, it could lead to severe engine difficulties. Coolant in the oil is particularly detrimental because it diminishes the oil's lubricating capacity.
Furthermore, you need to remember the various signs that can be an indicator that your oil coolers need to repair:
●Overheating of the engine or transmission: If your vehicle's engine or gearbox is prone to overheating regularly, this may indicate that the oil cooler is not operating as it should.
●Leaks: If you find oil leaks near the oil cooler, it may indicate damage or wear, indicating that the cooler needs to be replaced. Several different things can cause leaks.
●Low Cooling Performance: The cooling oil system has decreased performance. If you observe that the oil temperature is regularly higher than normal, this may be a sign that the oil cooler is not providing an adequate amount of cooling oil to the engine.
7 Benefits Of Oil Coolers
Whether installing an engine oil cooler in your vehicle is worthwhile relies on several things. To help you select, let's compare the advantages and disadvantages of engine oil coolers below.
The Oil Cooler Removes The Heat And Humidity
The most significant advantage of an engine oil cooler is the removal of excess heat from the motor oil. A steady supply of cool air flowing over the engine oil is essential. This is why it is usually preferable to have a larger opening through which air can pass. The temperature difference between the air and the oil is also important for cooling. Air at a lower temperature can be used to do this task more effectively than air at a higher temperature.
Engine oil coolers are small radiators positioned in front of a vehicle's coolant system, allowing the engine oil rapid access to the fresh, cool air generated by the cooling fan. These coolers decrease the oil's temperature as it travels through the coils. Remember that a motor oil cooler will only operate when the engine operates. Engine oil inspection is crucial among the many steps necessary to prepare your vehicle for warm weather. Reducing motor oil temperature has numerous benefits.
This is the greatest advantage of engine oil coolers. Added benefits of oil coolers include:
●As a result of the oil cooler's precise cooling of the engine's hot air, the engine's performance is enhanced.
●Oil cooling systems Ensure that the oil is properly cooled before circulating it.
●The water cooler controls the temperature of the oil.
●Easy to install of oil coolers
●Oil coolers reduce the use of corrosive engine-damaging water cooling systems.
●Oil circulation is regulated and effective.

8 What Are The Downsides Of Oil Coolers
Oil coolers have several benefits, such as preventing engine damage from overheating, but they also have some potential drawbacks, such as:
●It's possible that oil can catch fire.
●Extra oil is needed for the oil cooler to function.
In the event of an oil cooler failure, the coolant system could be overwhelmed, and the engine could overheat. The engine could be harmed as a result of this. If the leak is severe, you'll find coolant on the ground or observe steam coming out from under the hood.
These were the primary benefits and drawbacks of engine oil coolers. Please note that engine oil coolers do not reduce the temperature of the engine; they simply reduce the temperature of the engine oil. The engine is cooled exclusively by the vehicle's cooling systems.
Finally, returning to whether engine oil is worthwhile: Simply put, it relies on your motivation. You do not need an oil cooler if you drive your car to work every day and properly maintain it.
9 Tips To Install Oil Cooler
However, if you live in a particularly hot area, frequently traverse rugged terrain, and need a more powerful engine, it may be something to think about.
This concludes the data we know about engine oil coolers, including their benefits and drawbacks.
The negative is that front-mounted equipment like air conditioners, condensers, or transmission oil cooler can obstruct airflow. Remember that road debris is no friend to coolers, either. While a wheel well may appear ideal, the cooler could be damaged by tire shrapnel if it is not correctly installed.
Oil lines should have as few turns and as little length as possible.
A sandwich adapter features both the landing and filter, and an adapter, which utilizes a filter relocation kit, are two of the most effective techniques for adding and plumbing an oil cooler to an engine. The OEM filter is replaced with a round, two-port, O-ringed "puck," and its lines are rerouted to the filter cartridge mounting area. Always note that a sandwich adapter moves this same oil filter toward its bottom area and any other obstacles in its sections by the width of the sandwich adapter, which is around one but around a few inches closer to anything that is on the car driven near the filter.
It's common practice for those who have upgraded their engine to keep the temperature under the hood below 200 degrees Fahrenheit by installing a customized fan, a larger radiator, and other cooling-related parts. Customers ready to spend hundreds on new devices save thousands by adding an oil cooler. All of the aforementioned augmentations remain reliable options and industry standards for a reason. However, you plan on keeping your car for a while. An engine cooler is a cheap and effective long-term investment, especially compared to various climate control systems.
If the ECU determines that you do not require additional power, life will continue as normal.
However, the motor will receive current from the ECU if the latter determines that you require power assistance.
The motor is DC. It spins with a current. This then turns your steering column's reduction gear. You get power assist from this motion. Since the motor rotates the steering wheel, it will feel lighter.
10 In Conclusion
In summary, oil coolers are essential for maintaining the proper oil temperature in mechanical systems like engines and transmissions. They keep the oil just in its right viscosity and the oil temperature from damaging the system. The decision between air-cooled and liquid-cooled oil coolers is contextual, based on the needs and limitations of a given application. Oil coolers must be installed correctly to function properly and last as long as possible.
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?







Leave A Comment