Rack and pinion gears are a type of mechanical component used for converting rotary motion into linear motion or vice versa. They consist of a straight bar, called the rack, with teeth on one side, and a steering gear, called the pinion, with teeth around its circumference. When the pinion rotates, all the teeth engage with the rack and cause it to move in a linear direction.
This article will delve deeper into the working principles of rack and pinion gears, their design considerations, and their various applications. We will also explore some common rack and pinion gears and discuss their advantages and disadvantages.
1 What Is Rack and Pinion Gear?
A rack and pinion gear set can change the direction of a rotary motion into a linear one or vice versa. It comprises two major components: a straight bar with teeth on one side, known as the rack, and a round gear with teeth around its circle, known as the pinion. When the pinion rotates, it contacts the rack's teeth and causes the rack to move linearly.
Its linear motion can drive various systems or precisely control several applications. Common rack and pinion gear uses include automobile steering systems, robotics, industrial, and other applications requiring precise motion control. Their effectiveness and efficiency, small size, and user-friendliness make them popular in various industries.
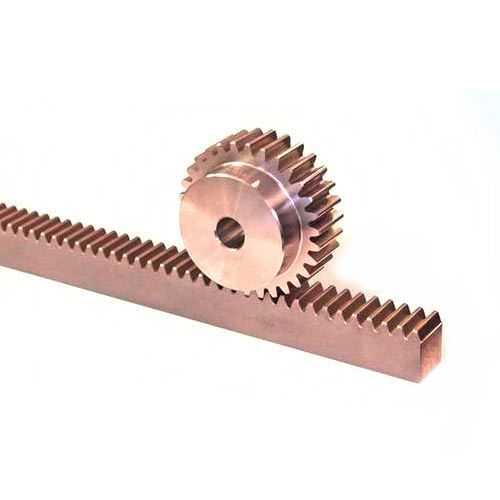

2 How To Use a Rack and Pinion Gear?
Now that you know what is rack and pinion, you will now learn to use them. Using a rack and pinion gear depends on the application for which it was built. Nonetheless, the fundamental operating principle is the same for all rack and pinion gears. Below are the basic steps for utilizing a rack and pinion gear:
Select your application's rack and pinion gear based on the required load capacity, speed, and precision.
●Install the gear system according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Normally, the pinion gear is attached to a motor or other rotating actuator while the rack remains stationary.
●Applying power to the pinion gear will result in its rotation. As the pinion rotates, its all teeth connect with the rack's teeth, causing the rack to move linearly.
●Use the rack's linear motion to drive other mechanisms or components as required. With a steering system, for instance, the linear movement of the rack is employed to turn the vehicle's wheels.
●Observing the operation of the rack and pinion for s10 gear system is functioning correctly.
While utilizing rack and pinion gears, always adhere to the manufacturer's recommendations and safety precautions.
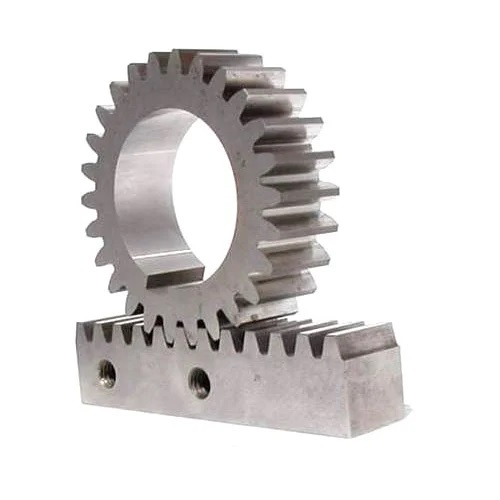

3 The Uses of Rack and Pinion Gear
Rack and pinion gears have many practical applications, making them essential components in various industries. Their ability to convert rotary motion into linear motion with high precision and efficiency makes them popular for many uses. From automotive steering systems to robotics, CNC machines to garage door openers, rack and pinion gears have transformed how we control and manipulate motion.
Due to their small size, great efficiency, and precise control, rack and pinion gears are frequently employed in several applications. Following are some typical applications for rack and pinion gears:
Vehicle Steering Systems
Modern automobiles frequently employ curved rack and pinion gears to transform the rotational action of the steering wheel into linear motion that turns the wheels.
Robotics
Robots employ rack and pinion gears to regulate the motion of robot arms, grippers, and other components.
Industrial Equipment
Rack and pinion gears are utilized in various industrial machinery, including conveyor systems, packing machines, and assembly lines.
Garage Door Openers
Garage door openers employ a rack and pinion for s10 gear to convert the motor's rotating motion into linear motion that opens and closes the garage door.
CNC Machines
In Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines, rack, and pinion gears are utilized to control the movement of the cutting tool along the X and Y axes.
Aerospace
Many aircraft components, such as flap actuators, landing gear systems, and control surfaces, utilize sweet rack and pinion gears.
Medical Devices
Medical devices such as surgical robots, imaging equipment, rehabilitation, rack, and pinion gears are utilized.
4 Different Types Of Rack And Pinion Gear
Each tool has multiple applications and nuances, so a rack and pinion gears system consists of two gears. The pinion gear is a conventional round gear, whereas the rack is straight or flat. The rack has teeth that interlock with the teeth of the pinion gear. The critical point of power transfer in a differential is a ring and pinion gear. There are three different varieties of rack and pinion gears.
Straight Teeth
Appropriate for general use with standard rpms. Here, the axis of the teeth and the axis of rotation are parallel. Typically, load transfer in Rack and Pinion systems is performed manually.
Helical Teeth
For precise applications, helical teeth are utilized; in this case, speed and load are significantly greater than in straight teeth applications. This type of Rack and Pinion gear is regarded as the most effective. The primary significance follows a helical path, and this type of gear features a continuous engagement along the length of the teeth. Helical teeth gears are less expensive but are subject to frequent wear and tear due to operating temperatures caused by side torque on the datums.
Roller Pinions
This form of Rack and Pinion utilizes rollers supported by bearings that mesh with the rack's teeth. It read, and its backlash to an almost nonexistent level.
The Pinion's diameter, thickness, width, manufacturer, etc., are essential for determining its servomotor, the density of the production material, etc. Typically, pinions are composed of steel, but aluminum is also occasionally employed.
Furthermore, the teeth Rack and Pinion require less driving force, resulting in a lower operating temperature, less friction, and reduced energy consumption.
The pitch of the gear tooth, the size of the Pinion gear (defined by the pitch circle diameter), and the gear ratio determine the most force delivered to this mechanism (the ratio of the number of rotations of a driver gear to the number of rotations of a driven gear).
Another way to classify curved rack and pinion is by the number of modules used. The gear module is obtained by dividing its pitch diameter (often measured in inches or millimeters) by its number of teeth. The Module of a gear denotes its size (large or tiny). A higher Module refers to a gear's higher forces and stiffness. Straight and helical racks offer several modular pitch options.

5 Rack And Pinion Gears System Fundamentals
Sometimes, a rack-and-pinion gear system (sometimes called rack-and-pinion gear system) is based on the conventional gear tooth type known as the 20° involute spur.
Formerly prevalent, involute spur gears with a pitch angle of 14-1/2° are no longer often used. These degree designations correspond to the pressure angle of the tooth, which is the contact line followed by two teeth as they enter and exit the mesh. Only with involute gears can the pressure angle remain constant during the meshing of each tooth. The involute tooth shape is brilliant because it ensures theoretically constant velocity ratios even if the center distances are not precisely determined. This requirement for a constant ratio of velocities is frequently called the fundamental law of gearing.
6 Common Problems Of Rack And Pinion Gears
While the steering is critical for managing your vehicle, diagnosing and remedying any steering faults is essential. Common steering issues include:
Very Snug Steering Wheel
Steering wheel resistance indicates a problem with the steering rack or a loss of pressure from the power steering unit if you've noticed it's getting harder to maneuver the vehicle. It may be as easy as adding more power steering fluid, but it's preferable to get it inspected.
Power Steering Fluid Leaking
If there is a leak, only then will the power steering fluid level decrewill ase, resulting in a tight steering wheel.
Steering Wheel Grinding Noise
Request that your mechanic examines the issue, as your steering gearbox may require replacement.
Burning Oil Smell
If you smell the odor of burning oil while driving, it indicates that the steering gear is overheated. It is advisable to pull over immediately and get the situation examined. Driving with a hot steering gearbox can result in a fire.
Repair
A rack and pinion steering system is typically easier to repair than a conventional system, and there are fewer potential points of failure or repair. Second, most mechanics should be familiar with it; you want someone else for repairs.
Lighter
Lowering its system components also decreases its mass. A few pounds might sound irrelevant, but when it comes to fuel efficiency or racing.
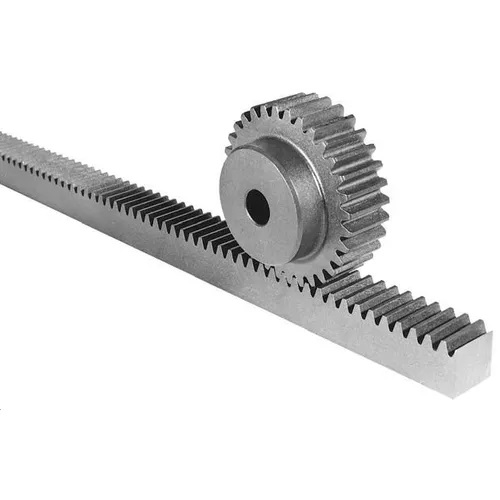

7 Factors To Consider When Using Rack And Pinion Gears
There are three primary kinds of rack and pinion gear systems.
Helical gears are more efficient and quieter than gears with straight teeth, and this is because their teeth mesh more gradually with the rack. Due to the longer contact length, helical gears can also carry heavier loads. Nevertheless, helical gears on parallel shafts provide a thrust component on both the rack and pinion gear due to their opposite hands. Thrust can introduce lateral loads to the structures of machines.
In contrast, roller pinion drives use a rack and pinion with bearing support rollers instead of traditional teeth, which mesh with a uniquely shaped rack.
They are meant to prevent backlash and, in some cases, eliminate it.
Generally, rack and pinion gear systems provide less mechanical power than other systems but compensate by offering greater feedback. A car's steering shaft provides a superior steering feel.

8 Benefits Of Rack And Pinion Gears
In any case, we've found that the usage of polymers in rack-and-pinion systems provides five important benefits:
Eliminates Lubrication.
As a self-lubricating polymer, Power-CoreTM eliminates the need to apply lubricants throughout the rack and pinion's lifetime. In delicate applications, such as packaging, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and food processing, the absence of lubricant reduces a significant source of contamination.
Extends Wearability
Stainless steel has a longer wear life and often outlasts all-metal designs by several years. Power-CoreTM users have also enabled us to develop design features that improve wear life, such as the pitch line control feature that prevents pinions from bottoming out.
This is a great way to extend the lifespan of your machine, especially if you are using it for business purposes. Wearability is a very big factor and you need to choose the right kind of gears. In this case, rack and pinion gears are what you need if you are into ensuring that your machine will last a really long time. This is what businesses should focus on, being able to extend the lifespan of machines so that the expenses would be lower.
Prevents Rusting
Especially in wet environments, the metal gearing in conventional rack and pinion designs can rust and corrode. As a polymer, Power-CoreTM is entirely corrosion-resistant.
Dimensionally Consistent
Due to the physical qualities of its base polymer, Power-Core is not susceptible to the changes in dimensions and tensile strength that impact traditional polymers when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or elevated temperatures. The core's polymer has one of any engineering plastic's lowest water absorption rates, and Power-CoreTM is resistant to various industrial chemicals. And Power-CoreTM is approximately 50% more effective at high temperatures than comparable engineering polymers.
Increases Motion Control.
While the rack travels back and forth, Power-CoreTM can provide rack-and-pinions that work smoothly and silently, decreasing noise by about 6 dB compared to all comparable components. The polymer has inherent vibration and shock load-damping characteristics. In addition, Power-CoreTM components weigh about less than comparable metal components, and this weight reduction directly reduces moving mass and moment of inertia. This is also one of the best ways to reduce fuel consumption because your machine doesn’t create different movements and motions which aren’t needed or necessary. Being able to control the motion in a very specific manner is important if you want to ensure utmost efficiency and productivity in your machine.
High Precision
Its mechanism's gears mesh without any loss of precision. Thus the teeth will always mesh appropriately for smooth operation. This results in higher efficiency when used to systems with high speed and power demands, such as traction drive systems, opening automobile hoods, and powering swing doors.
Consistency In Results
No slippage or sliding, as in cam or lever systems, means that torque is maintained throughout the system's range of motion.
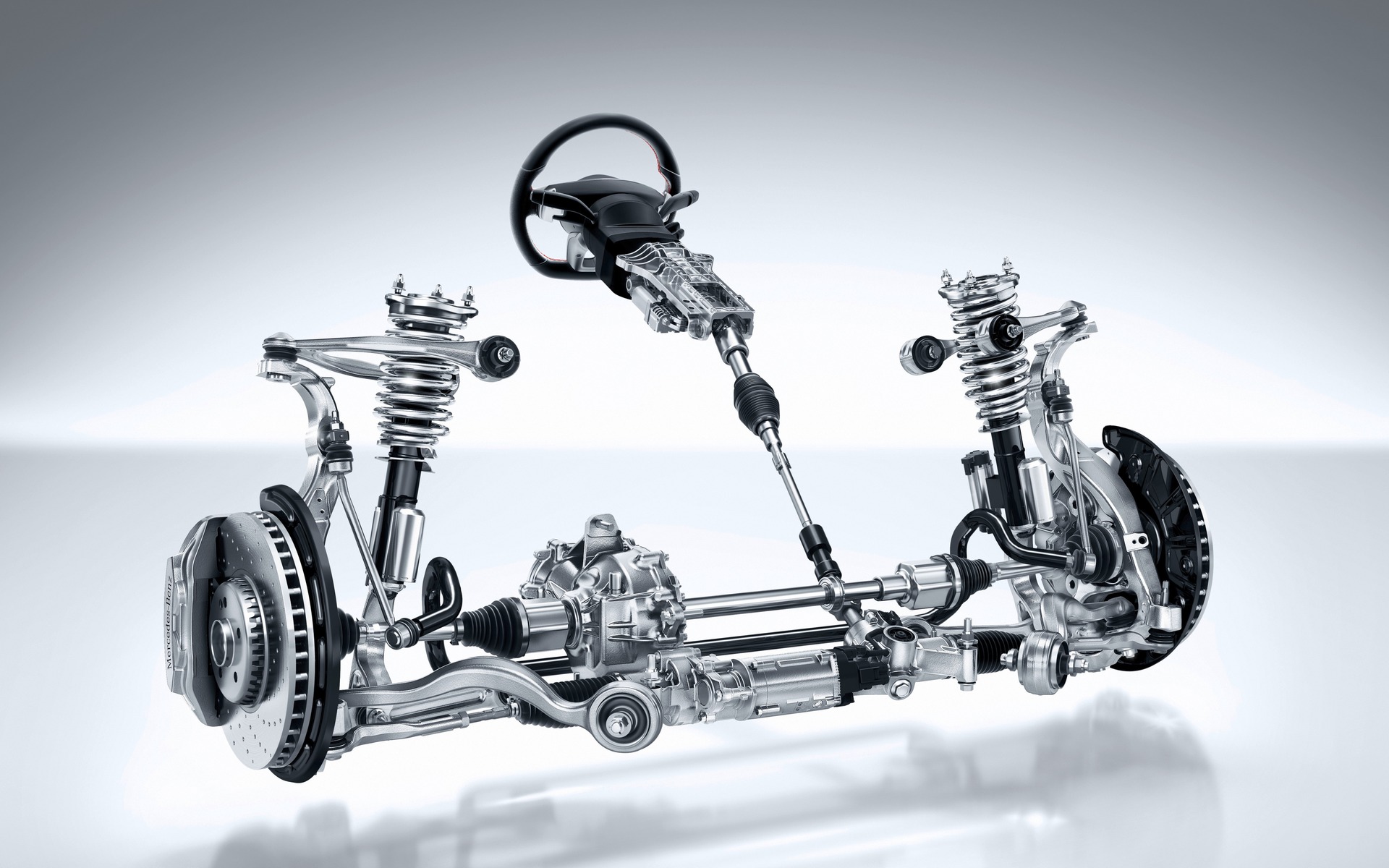
9 Disadvantages Of Rack And Pinion Gears
Several vehicles include rack and pinion steering. In essence, the steering wheel rotates a round gear, the pinion, which in turn might bar with gear teeth, the rack, from side to side to turn the wheels.
Leakage
However, this increases the stress on the individual components, and the resulting wear might lead to leakage, necessitating the replacement of the rack assembly.
Less Durability
Off-roading with a four-wheel-drive vehicle equipped with rack and pinion steering might be problematic. While this simple technique provides responsive handling on concrete roads, the increased force necessary to turn the wheels on highly uneven terrain may deteriorate considerably more rapidly.
Vibration
Because of the fewer moving components and the more straightforward design of rack and pinion systems, they can give a more natural and responsive steering experience. Yet, this closer proximity to the road can transmit more noise and vibration to the driver and passengers.
Unable To Provide Exact Linear Motion
The conventional mechanism cannot produce linear motion since its teeth are not designed to mesh. This renders it unsuitable for use in systems requiring precise movements, such as cams and actuators.
Severe Deterioration Over Time
This type of equipment endures considerable wear and tear when in operation, especially if it is not adequately maintained (which is highly recommended in rack and pinion systems). The friction between its meshing elements might generate heat, resulting in the early failure of its components.
Insufficiently Flexible For All Uses
While this gear type works well with most gearchange mechanisms, it does not perform better with systems that need high speeds and precision, such as traction drive systems, opening car hoods, and powering automobile doors.
This shows that you really need to choose the right kinds of gears to ensure that your machine and equipment will function properly and without fail. What’s also nice with ensuring flexibility is that you are able to ensure that your machine can handle various shapes and sizes without having to worry about compatibility issues beforehand.
10 In Conclusion
In conclusion, rack and pinion gears are vital to many mechanical systems, such as automotive steering systems, machinery, and robots. They offer a dependable and effective method of transferring rotational motion to linear motion and vice versa.
Overall, rack and pinion gears effectively transmit power and motion in several mechanical systems, and their utility and adaptability will continue to make them a popular option. For sure, the use of rack and pinion gears will increase in the years to come especially that this is the most cost-efficient and durable option to choose.
The Previous Articles:
What Is Rack and Pinion Bushing? How To Tell If Rack and Pinion Bushings Are Bad?
Why Steering Rack Makes Noise When Turning?
How To Rebuild A Steering Rack?
What Is A Rotary Valve Power Steering Rack?
Rack And Pinion System Vs Power Steering System: What Are The Differences?
Power Steering Rack Market Analysis Report (Japan Market)
What Causes Steering Rack to Go Bad?
Design Of Car Rack And Pinion Steering Racks
What Is The Intelligent Steering Rack Used By VW, Toyota, Honda And Renault?







Leave A Comment